Companies register activities: 2019 to 2020
Published 25 June 2020
1. Introduction
This release provides information about the population of companies and corporate bodies in the UK. Companies and corporate bodies are specific legal forms of business that are registered at Companies House. Companies form a subset of corporate bodies and are formed under the Companies Act 2006. Companies and corporate bodies are registered at Companies House regardless of whether they go on to trade actively. Full definitions of both companies covered by the Companies Act 2006 and corporate bodies are provided in the separate Companies House official statistics: definitions to accompany statistical releases document. This document also explains the incorporation, dissolution and restoration processes.
This release complements the quarterly Incorporated Companies in the UK release by providing information on both companies to which the Companies Act 2006 relates, and on wider corporate body types. Sections 2 to 4 of the release focus specifically on companies, while sections 5 and 6 cover all corporate body types. Some figures in this release may differ to those provided in the quarterly Incorporated Companies in the UK publications due to the timing of the analysis. Analyses for the figures in this release are undertaken later in the year, allowing more information to be processed and added to the register.
The statistics in this release include the total number of incorporated companies, newly incorporated companies, and the number of companies that were dissolved. The release focusses on the headline messages for the UK: figures for the constituent countries are contained in the supplementary tables that accompany the release.
Key points
-
The total register size at the end of March 2020 was 4,350,913, an increase of 3.5% when compared with the end of March 2019.
-
Between 2018 to 2019 and 2019 to 2020, register growth has slowed (3.5%) when compared with the average growth of the previous 5 years (5.3%).
-
There were 665,495 company incorporations in 2019 to 2020. Whilst this is a decrease of 1.1% when compared with 2018 to 2019, it’s the second highest number of incorporations since UK figures were first reported, in 2009 to 2010. The decrease mainly relates to there being an unusually high number of incorporations during 2018 to 2019.
-
In 2019 to 2020, there were 536,934 dissolutions in the UK, a year on year increase of 5.5%. This is the largest number of dissolutions since 2009 to 2010. However, this was influenced by figures relating to the end of the financial year. During March 2020, the number of dissolutions increased considerably when compared with March 2019. The observed increase in March 2020 coincides with the emergence of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic.
-
The average age of a company on the total register at the end of March 2020 was 8.7 years. Despite fluctuations in recent years, the average age of a company has gradually declined from 10.7 years at the end of March 2000.
-
Since 2004, private limited companies have consistently accounted for over 96% of all corporate body types. During this time, the three corporate bodies accounting for the highest proportion of all corporate bodies have remained unchanged. These are private limited companies, limited partnerships and limited liability partnerships.
-
At the end of March 2020, the number of overseas corporate bodies on the register with a physical presence in the UK increased when compared with the end of March 2019, reaching 12,300. The largest share of overseas corporate bodies on the register originated in the USA, which accounted for 20.9% of all overseas companies.
2. Incorporated companies
The total register size – including those in the process of dissolution and liquidation (286,850) – at the end of March 2020 was 4,350,913. This is an increase of 3.5% when compared with the end of March 2019. The effective register, which does not include those in the process of dissolution or liquidation, at the end of March 2020 was 4,064,063.
The total register increased in size across all constituent countries of the UK – England and Wales increased by 3.5%, Scotland increased by 3.3% and Northern Ireland increased by 5.5%.
Figure 1: The number of companies by region at the end of March 2020
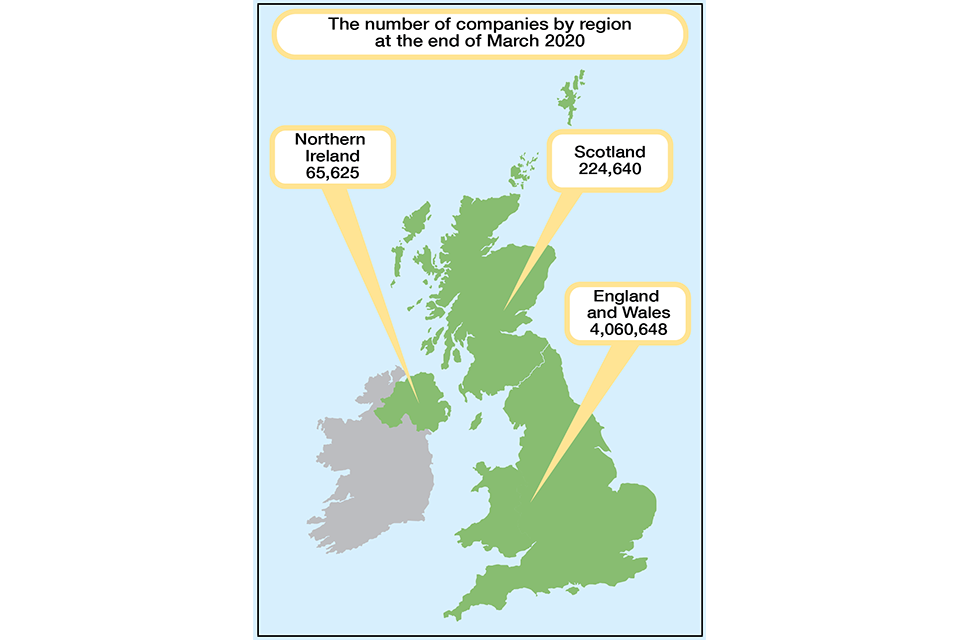
Source: Companies register activities, 2019 to 2020, Companies House.
During 2019 to 20, there were 665,495 company incorporations, a year on year decrease of 1.1%. It’s worth noting, however, that during the previous year, there were an unusually high number of incorporations. When comparing 2019 to 2020 with 2017 to 2018, the number of incorporations increased by 45,210 (7.3%). However, during March 2020, there was also a noticeable decrease in the number of incorporations compared with March 2018. The observed decrease in March 2020 coincides with the emergence of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic.
At the end of March 2020, incorporations decreased by 7,069 (1.1%) in England and Wales when compared with the previous year, whilst Scotland decreased by 731 (2.2%). Northern Ireland saw the only percentage increase of 5.0%, an increase of 405 incorporations.
In the same year, there were 536,934 dissolutions, an increase of 5.5% compared with 2018 to 2019. However, during March 2020, there was a considerable increase in dissolutions when compared with March 2019. This increase also coincides with the emergence of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic.
The highest rate of increase in the number of dissolutions in 2019 to 2020 were found in Northern Ireland (17.2%), followed by England and Wales (5.5%) and Scotland (2.9%).
Despite fluctuations, the number of incorporations and dissolutions over time have increased at a steady rate. There were 547,695 more incorporations in 2019 to 2020 compared with the number of incorporations in 1986 to 1987, when the reporting of financial-year data began. There were 452,734 more dissolutions over the same period.
Chart 1: UK incorporations and dissolutions from 1979 to 2020
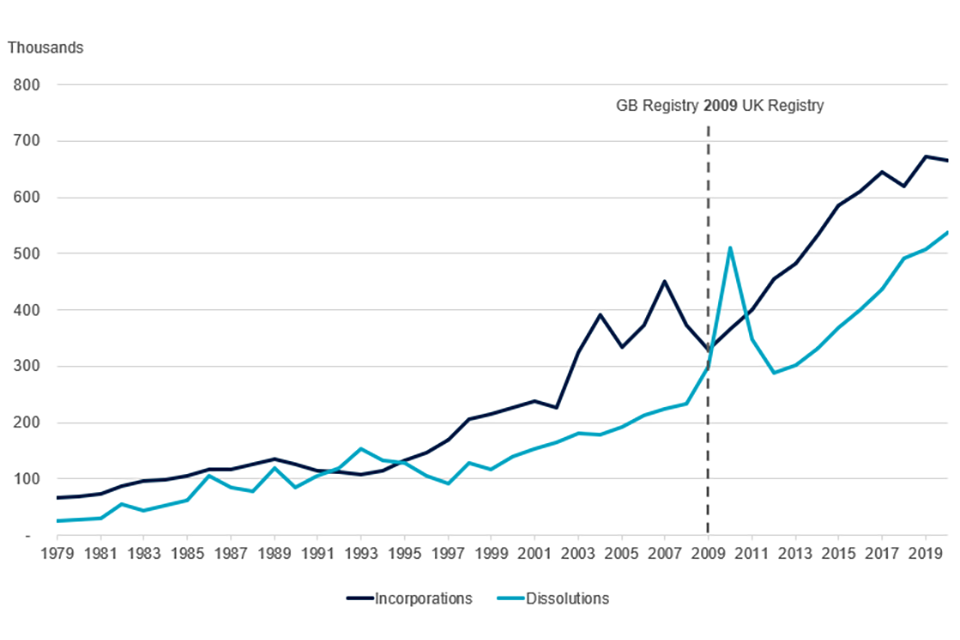
Source: Companies register activities, 2019 to 2020, Companies House.
A full breakdown of figures for England and Wales, Scotland, Northern Ireland and the UK as a whole is provided in Table A1 in the Excel workbook that accompanies this release. Figures are provided for the years 2012 to 2013 through to 2019 to 2020. Separate figures for private companies and public limited companies are provided in Tables A2 and A3, respectively.
3. The growth in the register size over time
Between 1979 and 2020, the total register has increased by 3.6 million companies, whilst the effective register has increased by 3.3 million companies[footnote 1], [footnote 2].
During this time, the total register has seen 37 annual increases, whilst the effective register has increased 35 times over the same period. The most recent declines in the Great Britain effective register occurred in 2008 to 2009, with a decrease of 157,700 companies. The UK total register declined a year later in 2009 to 2010, with a decrease of 88,316 companies.
In the late 2000s, it was anticipated that the register size would increase due to the introduction of Northern Ireland companies to the UK register. However, this may have been offset by the global financial crisis at a similar period leading to a slight decrease in the register size overall.
During the period 2009 to 2010 there were also several significant changes to the register:
-
the Northern Ireland register was included to create a UK register, as mentioned above.
-
there was a change in the administrative system that forms the register.
-
there was a purge on the register to remove defunct companies that had spent an extended period in the process of dissolution or liquidation.
-
legislative changes were introduced under the Companies Act 2006, which reduced the time taken to dissolve companies and remove them from the register.
These changes in combination are likely to have contributed to a sharp increase in the number of dissolutions between 2009 and 2010. This may in turn have had an impact on the sizes of the total and effective registers overall.
Since 2010 to 2011, both registers have continued to increase in size in a steady fashion, albeit at a slower rate in recent years.
Between 2012 to 2013 and 2019 to 2020, the average growth rate for the total and effective registers was 5.2% and 5.6%, respectively. During 2019 to 2020, the growth rates of both slowed to 3.5%.
Chart 2: UK total and effective register sizes from 1979 to 2020
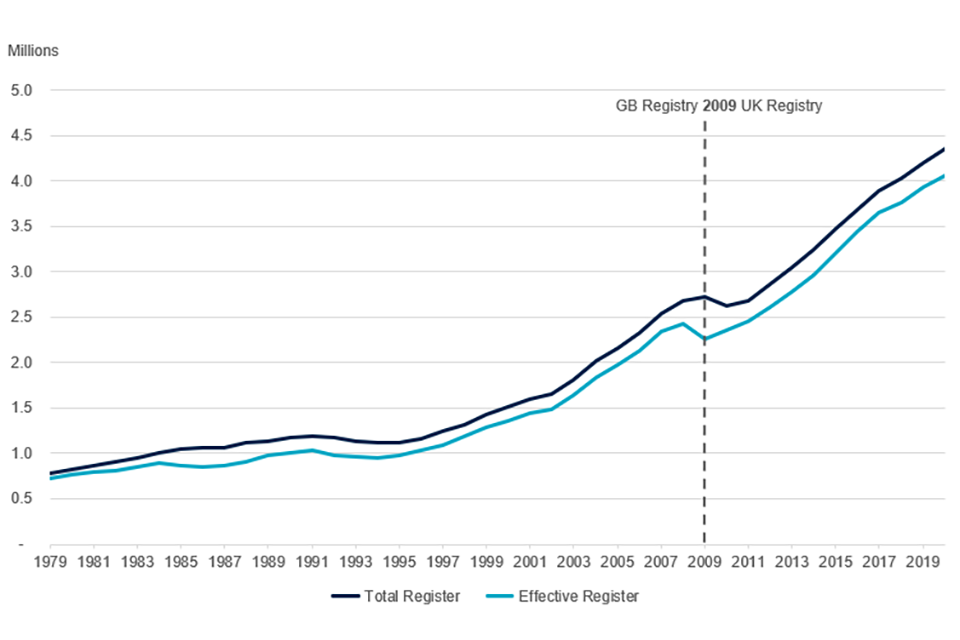
Source: Companies register activities, 2019 to 2020, Companies House.
Table A8, in the workbook that accompanies this publication, shows the total and effective register sizes from 1939 to 2019-20, as well as the annual number of incorporations, dissolutions and liquidations.
4. Age of companies on the register
The average age of UK companies on the total register in 2019 to 2020 was 8.7 years, an increase compared with the previous year of 8.5 years. Within both the total and effective registers for 2019 to 2020, almost half of the companies were aged under 5 years (47.1%).
Over two-thirds (70.4% for the total register and 70.3% for the effective register) were under 10 years, whilst just over one in ten companies were aged over 20 years on both the total and effective registers (10.6% and 12.3%, respectively).
Chart 3: Age profile of companies on the total UK register for 2020
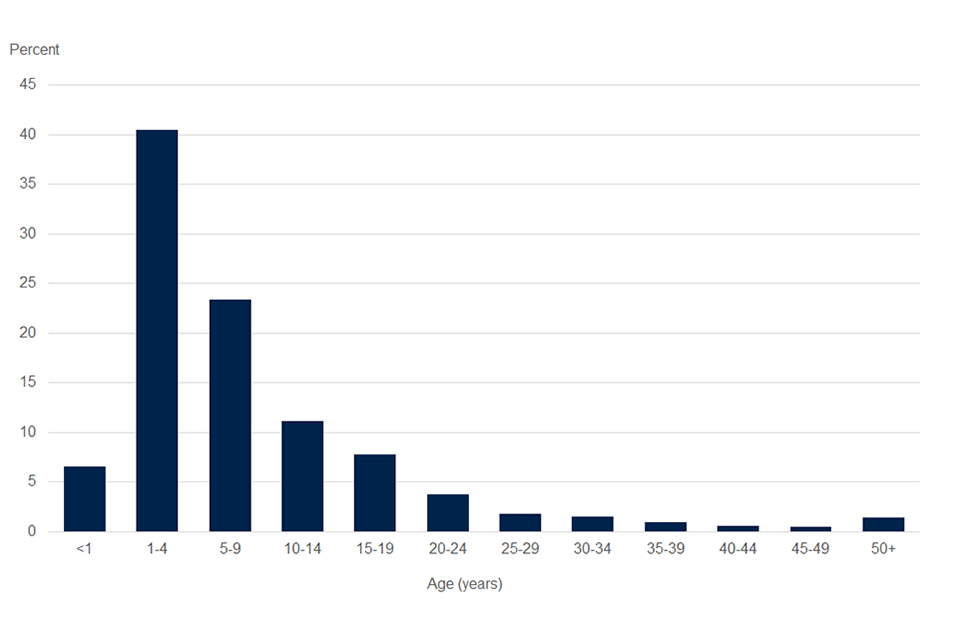
Source: Companies register activities, 2019 to 2020, Companies House
Historically, the average age of a company has always been relatively young. However, the average age has gradually declined from 10.7 years in 2000 to 2001 to 8.7 years in 2019 to 2020. Between 2008 to 2009 and 2010 to 2011, the average age of a company fluctuated. This corresponds with changes in the numbers of incorporations, dissolutions, and in the overall register size.
Since 2000 to 2001, the steady decline in the average age of a company could be due to the general increasing trend we have seen in the number of incorporations and dissolutions. It’s likely that the increasing number of incorporations has led to a greater number of younger companies on the register, which has served to lower the average age of companies overall.
The average age of a dissolved or closed company has declined from 5.7 years in 2012 to 2013 to 5.0 years in 2019 to 2020, consistent with the previous year.
Chart 4: Average age of a company on the total UK register from 2000 to 2020
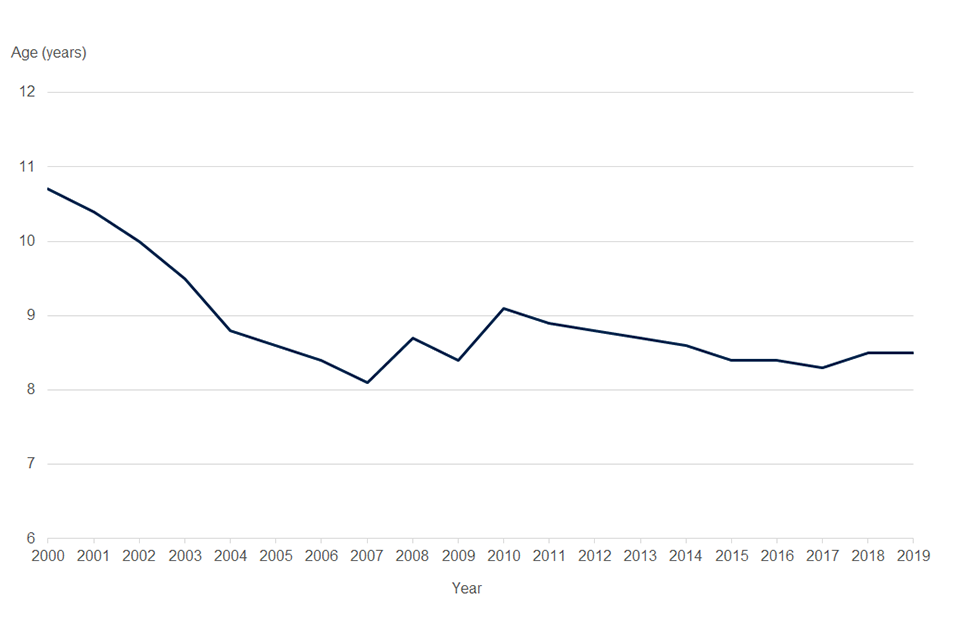
Source: Companies register activities, 2019 to 2020, Companies House.
Table A5, in the workbook that accompanies this release, shows the age profile of companies on the total and effective registers at 31 March 2020, as well as those in liquidation or the course of dissolution. The table also shows the average age of a company from 2000 to 2001 to 2019 to 2020. Table A11 shows the average age of dissolved and closed companies from 2012 to 2013 to 2019 to 2020, while Table C3 shows average ages at closure and dissolution across all corporate body types.
5. Types of corporate body on the register
There are 28 types of corporate body held on the register. These include a number of corporate body types in addition to those companies covered by the Companies Act 2006.
Each corporate body type has a distinct set of requirements, as outlined in various pieces of legislation and royal acts. This information is provided to Companies House. Further information on each company type can be found in the Companies House guidance.
Since 2004, private limited companies have consistently accounted for over 96% of all corporate body types. During this time, the three corporate bodies accounting for the highest proportion of all corporate bodies have remained unchanged. These are private limited companies, limited partnerships and limited liability partnerships (LLPs).
These three corporate body types have consistently accounted for over 98% of all corporate body types.
Table 1: Breakdown of corporate body types on the UK total register for 2019 to 2020
| Corporate body type | Number | Percentage of all corporate bodies |
|---|---|---|
| Private Limited | 4,183,970 | 92.8 |
| Private Limited by Guarantee/No Share Capital | 115,142 | 2.6 |
| Limited Partnership | 53,273 | 1.2 |
| Limited Liability Partnership | 51,154 | 1.1 |
| Private Limited by Guarantee/No Share Capital/(Use of Limited Exemption) | 41,201 | 0.9 |
| Charitable Incorporated Organisation | 21,351 | 0.5 |
| Overseas Company | 12,668 | 0.3 |
| Registered Society | 10,906 | 0.2 |
| Public Limited Company | 6,198 | 0.1 |
| Other corporate body types | 12,038 | 0.3 |
| Total of corporate body types | 4,507,901 | 100.0 |
Although the composition of the register overall has remained stable, there have been some minor fluctuations within the individual company types:
-
Charitable Incorporated Organisations (CIOs) were introduced in late 2017. The Charity Commission allowed charitable companies to convert to CIOs. This is an incorporated structure designed for charities and needs to be registered with the Charity Commission. For the financial year of 2019 to 2020, there were 21,351 CIOs in England, Wales and Northern Ireland (0.5% of all corporate bodies) and 4,420 Scottish CIOs (0.1% of all corporate bodies). Since 2017/18, the number of CIOs has increased, with average annual growth rates in England, Wales and Northern Ireland being 24.9%, whilst Scotland has seen an average annual growth rate of 15.6%.
-
Limited liability partnerships (LLPs) were introduced in 2001. These gradually increased in number to make up 1.8% of the register in the years 2012 to 2014. The proportion of LLPs has since gradually declined, and they now account for 1.1% of the register.
-
Limited partnerships have grown from 0.5% of the register at the end of 2004 to 1.2% at the end of March 2020. This has been primarily due to large increases in the numbers of limited partnerships in Scotland between 2012 and 2013 and they continue to make up a large share of limited partnerships on the register.
-
Public limited companies have been declining in number since 2008. They now make up only 0.1% of the register overall.
Although these changes are small, they show the subtle ways in which the composition of the register is changing outside of private limited companies.
Table C1, in the workbook that accompanies this publication, displays numbers and percentages of all corporate body types on the register from 2004 to 2020. Further information on public limited companies, limited partnerships and limited liability partnerships is available in tables A3, B2 and B4, respectively.
6. Overseas corporate bodies with a physical presence in the UK
At the end of March 2020, there were 12,300 overseas corporate bodies on the total register.
Overseas corporate bodies are incorporated outside of the UK but have a physical presence in the UK (such as a place of business or branch) through which they carry out their business.
At the end of March 2020, the largest share of overseas corporate bodies on the register originated in the USA. This accounted for 2,575 (20.9%) of all overseas companies. The Republic of Ireland, the second highest originating country, accounted for 1,094 (8.9%).
The top 10 countries incorporating corporate bodies in the UK in 2019 to 2020 are consistent with those of the previous year. These countries accounted for 63.2% of all overseas corporate bodies on the total register at the end of March 2020.
Figure 2: Top 10 originating countries for overseas corporate bodies, 31 March 2020
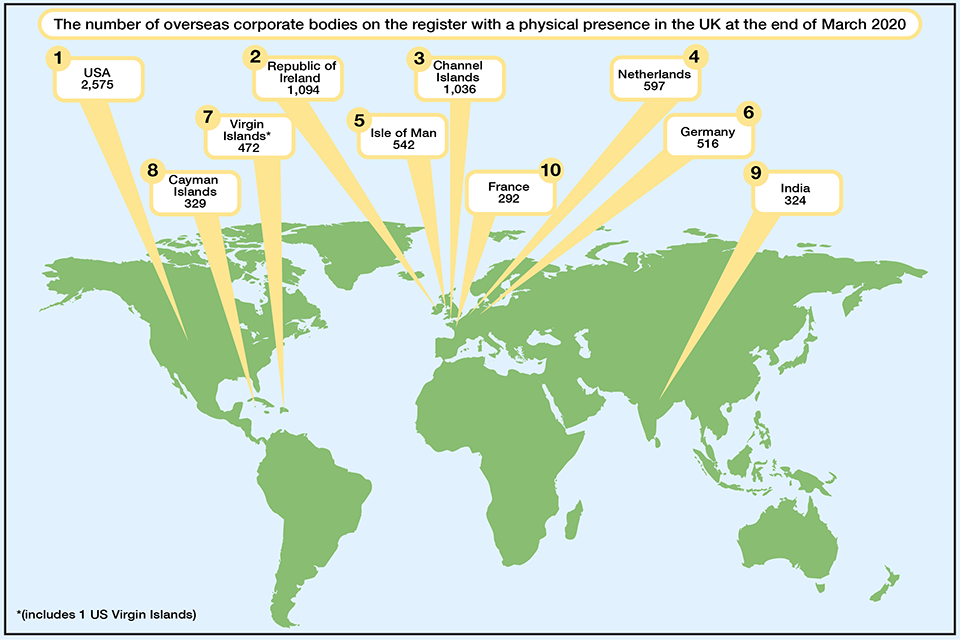
Source: Companies register activities, 2019 to 2020, Companies House.
There were 903 new incorporations for overseas corporate bodies in 2019 to 2020. Of these, 169 (18.7%) originated in the Channel Islands, 117 (13.0%) in the Republic of Ireland, and 93 (10.3%) in the USA.
These three countries have consistently had the highest numbers of new incorporations since 2013 to 2014.
Table 2: Registrations of corporate bodies incorporated outside the UK in 2019 to 2020 for the top 10 originating countries
| Country of incorporation | New incorporations | Percentage of all incorporations |
|---|---|---|
| Channel Islands | 169 | 18.7 |
| Republic of Ireland | 117 | 13.0 |
| USA | 93 | 10.3 |
| Isle of Man | 34 | 3.8 |
| Netherlands | 34 | 3.8 |
| Germany | 30 | 3.3 |
| Virgin Islands (includes 1 US Virgin Island) | 27 | 3.0 |
| France | 22 | 2.4 |
| Italy | 21 | 2.3 |
| Belgium | 19 | 2.1 |
| Total | 566 | 62.7 |
Full figures on registrations of corporate bodies incorporated outside the UK from 2013-14 to 2019-20, as well as numbers on the register at 31 March 2020, are provided in table B1.
7. Other statistics in this release
A range of other statistics are included in the tables that accompany this release, including:
- analysis of companies on the register by period of incorporation
- removals of companies from the register
- other corporate bodies administered at Companies House, including limited partnerships and limited liability partnerships
A range of management information tables are due to be published later in the summer, providing information on:
- civil penalties for late filing of annual accounts
- disqualification orders notified to the Secretary of State in the UK
- prosecutions by the department under the Companies Act 2006
- number of documents filed at Companies House
- annual accounts registered at Companies House by accounts type
8. Background notes
This section provides a range of information designed to provide the user with more information about the statistics.
Definitions
A separate document is available providing definitions for the main terms used in Companies House official statistics publications.
Quality
Information relating to the quality of the statistics is provided in a separate quality document. This document provides information on the quality of Companies House’s official statistics, to enable users to judge whether or not the data are of sufficient quality for their intended use. The information is structured in terms of the quality dimensions of the European Statistical System. The document also provides information on how these statistics relate to selected other business statistics.
Coverage
This release provides information on the size of the company population and the changes that have occurred within the year. The release includes statistics for the UK, England and Wales, Northern Ireland, and Scotland. The statistics cover companies and corporate bodies, both of which are specific legal forms of businesses that are registered at Companies House. They do not include information on sole proprietorship businesses, partnerships, and charities.
Use and users
Companies House statistics are used extensively by government, the public, public bodies and businesses. For example, they’re used by:
- government in understanding the likely impact of policy changes and monitoring the impact of economic changes on companies
- businesses in understanding their market share and planning marketing strategies
- banks in developing an understanding of their customer base
- foreign firms in making UK location decisions
- academics to inform research into businesses at local and national level
- a range of public bodies in decision making and evaluating business-related policies
Revisions to these statistics
Revisions to these statistics will be mainly due to changes in methodologies and source data. The statistics are derived from administrative data, and changes to the underlying methods will cause revisions. These include changes in statistical methods, definitions, classifications, and geographic coverage.
Although Companies House has robust procedures in place to minimise errors in the methods used to create these statistics, errors may occasionally occur. If errors are found after the publication, their impact will be assessed. If the changes are significant, a corrigendum will be issued as soon as possible. Minor corrections will be included in the next planned release.
Any misleading or incorrect figures will be amended, and a footnote added to indicate that the figures have been corrected. The nature and reason for the correction will be explained.
Date of next release
Statistics for the 12 months to March 2021 will be published 24 June 2021. The publication date will be announced on our release calendar.
-
Statistics for 1979 to 2008 are for Great Britain. In October 2009, the Northern Ireland register merged with the register for Great Britain to create a UK register. Figures from 2009 to 2010 onwards are for the UK as a whole. ↩
-
Figures for 1979 to 1986 are for the calendar year 1 January to 31 December. Those for 1986 to 1987 to 2019 to 2020 are for the financial year 1 April to 31 March. ↩
