OCT examples
Updated 16 April 2025
Applies to England
1. High risk maculopathy
High risk maculopathy is defined as macular exudation (circinate) greater than 1/2 disc area, within 1 disc diameter (DD) of the fovea and a drop in visual acuity in this eye to less than or equal to 6/12.
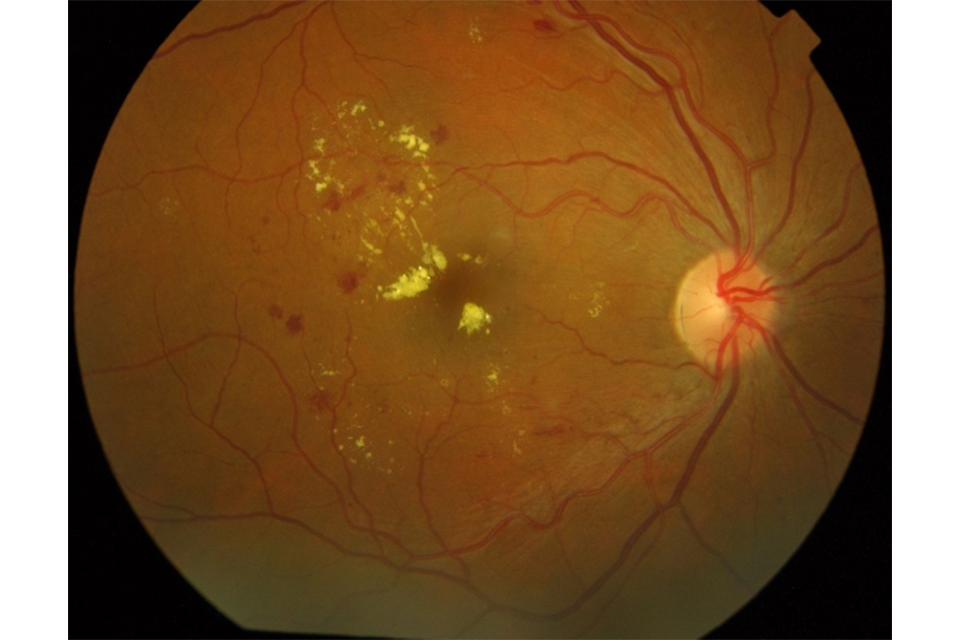
High risk maculopathy
2. OCT negative
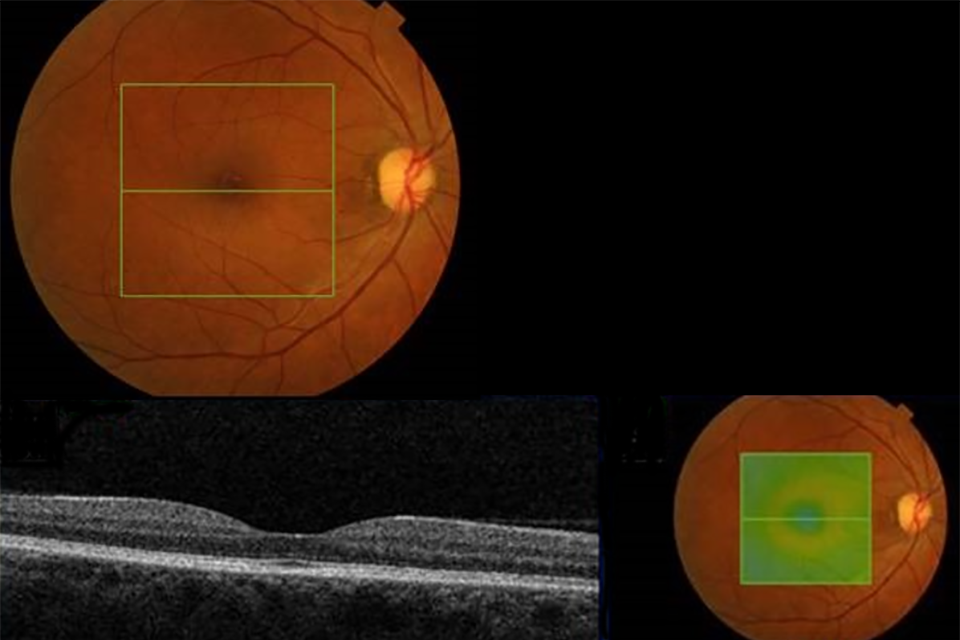
Example 1 R1M0 and OCT negative
Example 1 has no:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1
- intraretinal cysts
- change in foveal contour
- diffuse thickening
Discharge back to routine screening.
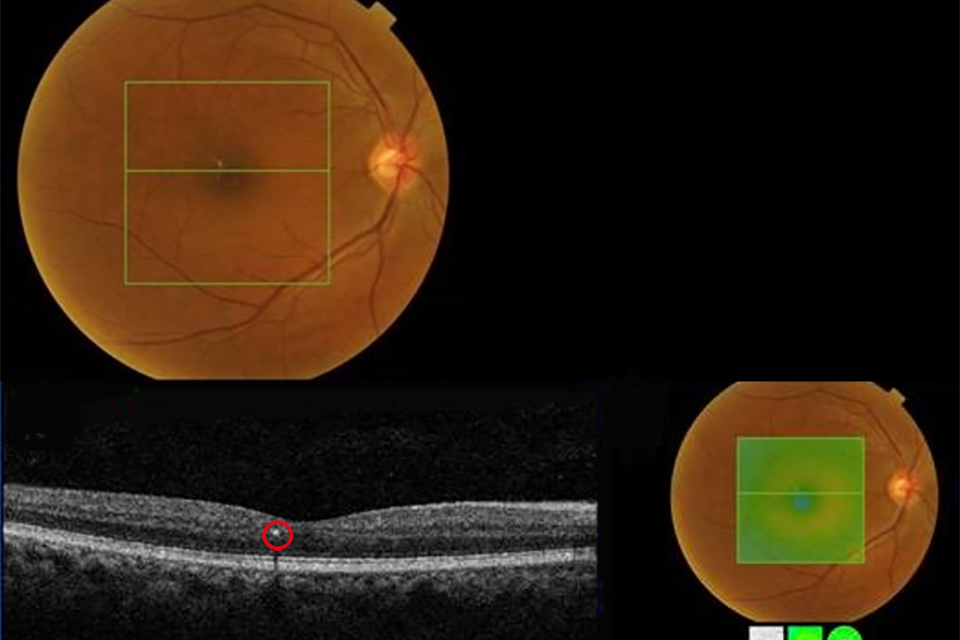
Example 2 R1M1 and OCT negative with exudate circled in red
Example 2 has:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1, for example exudate within 1 DD
- no intraretinal cysts
- no change in foveal contour
- no diffuse thickening
If the surrogate marker for M1 is due to microaneurysms or haemorrhage within 1 DD of the centre and a visual acuity (VA) of 6/12 or worse, the OCT grader can return these to routine digital screening (RDS) if they believe the reduced vision is not due to diabetic maculopathy. In these cases, the M1 would be downgraded to M0 and relevant notes made in the screening episode to support the decision.
Outcome: follow up in digital surveillance (DS).
3. OCT borderline
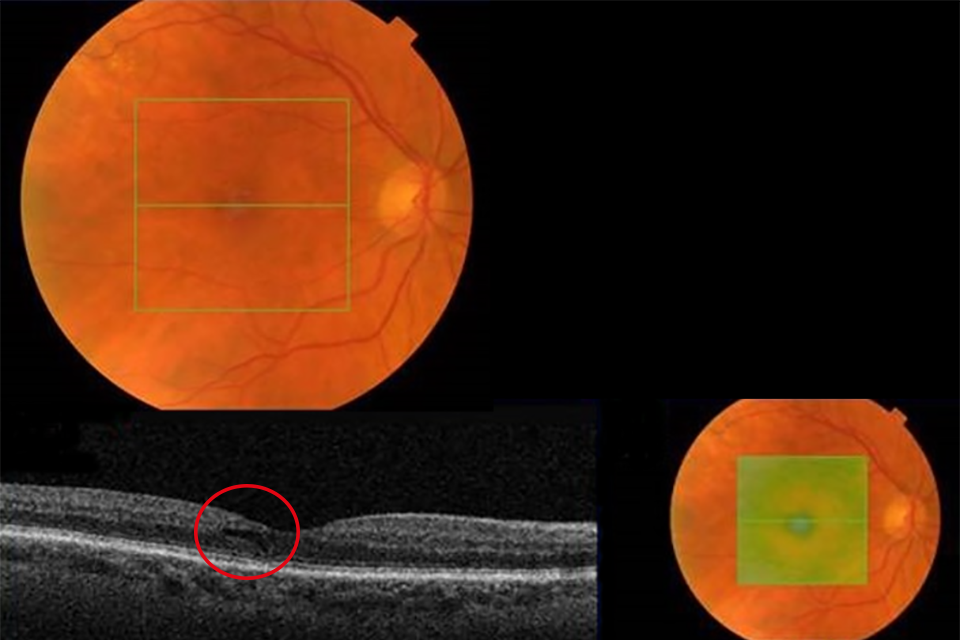
Example 3 R1M1 and OCT borderline with intraretinal cysts circled in red
Example 3 has:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1
- intraretinal cysts
- no change in foveal contour
- no diffuse thickening
Outcome: follow up in DS.
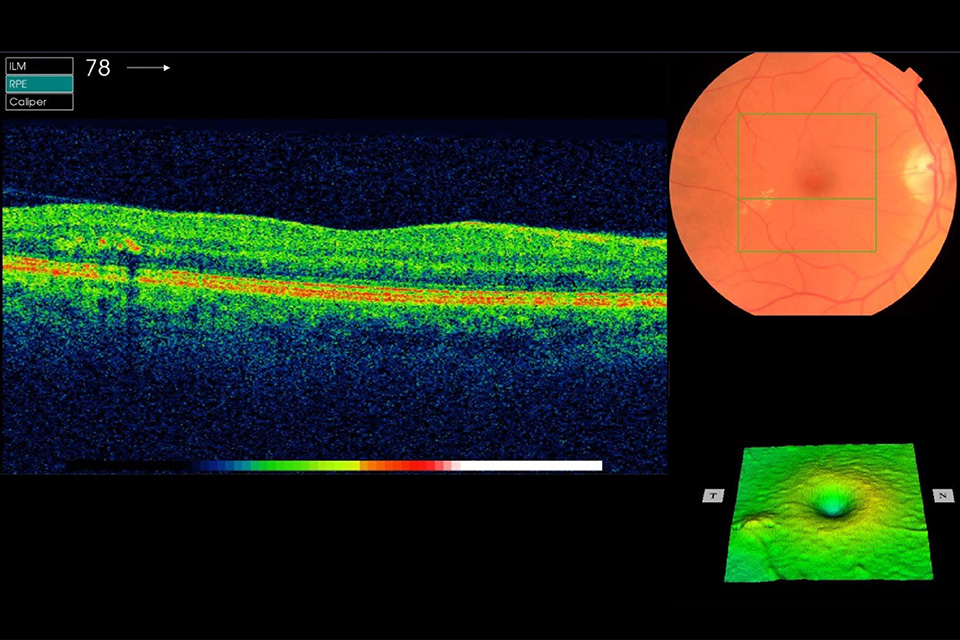
Example 4 R1M1 and OCT borderline. No change in foveal contour but retinal thickening (less than 1 DA), the edge of which is more than 1 disc diameter from the central fovea but within the definition of macula
Example 4 has an area of retinal thickening less than 1 disc area within the NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme definition of the macula. It has:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1
- intraretinal cysts
- no change in foveal contour
- retinal thickening (less than 1 DA) the edge of which is more than 1 disc diameter from the central fovea but within the NDESP definition of macula
Outcome: follow up in DS.
4. OCT positive
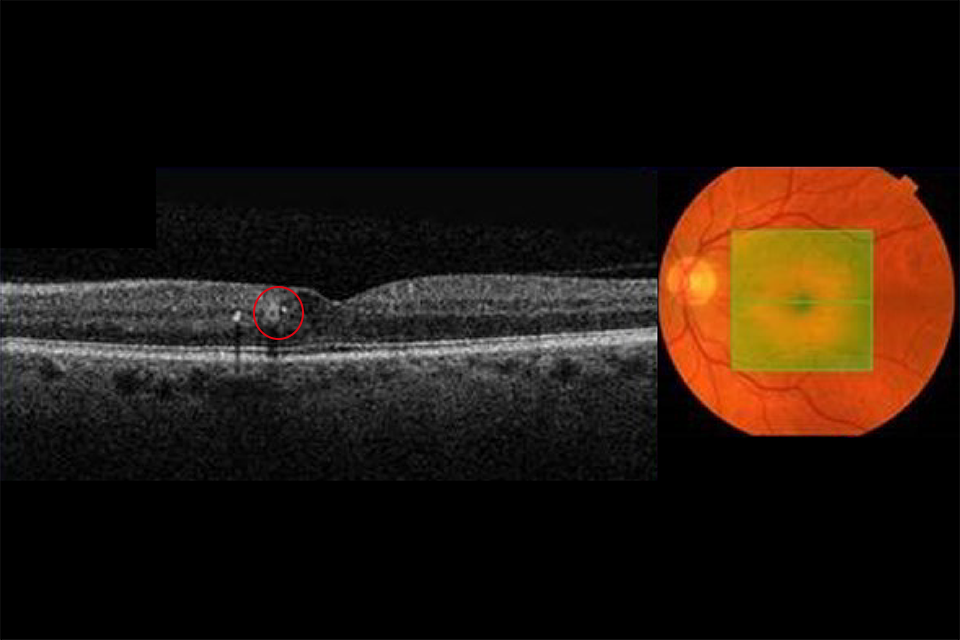
Example 5 R1M1 and OCT positive. Change in foveal contour with intraretinal cysts and exudate circled in red
Example 5 (slight change in foveal contour) has:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1
- intraretinal cysts
- slight change in foveal contour
- no diffuse thickening
Outcome: referral to HES (unless extenuating circumstances requested by clinical lead).
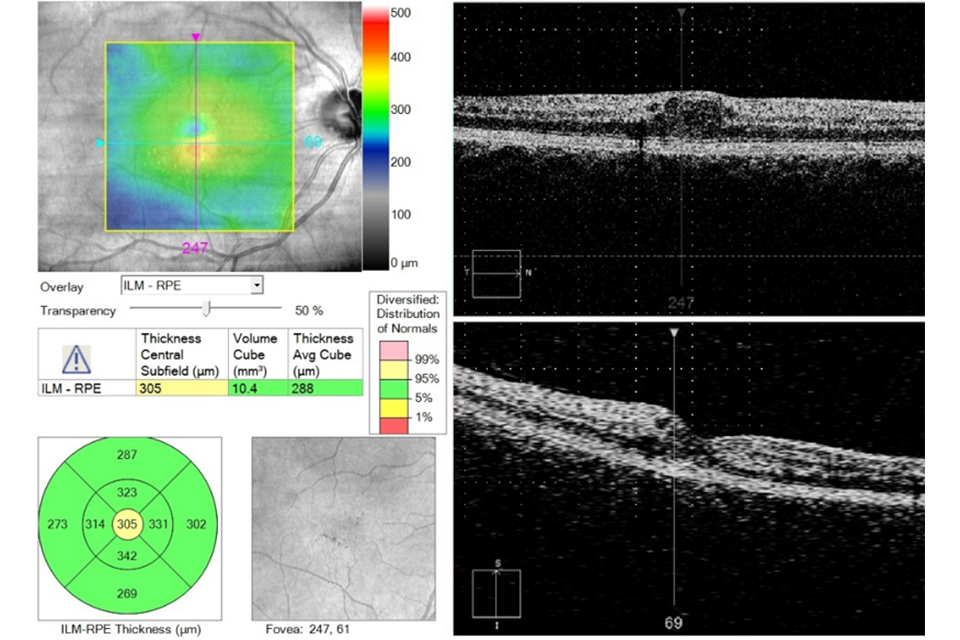
Example 6 R1M1 and OCT positive. Early thickening inferior to fovea and change in foveal contour with intraretinal cysts
Example 6 (parafoveal thickening and change in foveal contour) has:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1
- intraretinal cysts
- change in foveal contour
- early parafoveal thickening
Outcome: referral to HES (unless extenuating circumstances requested by clinical lead).
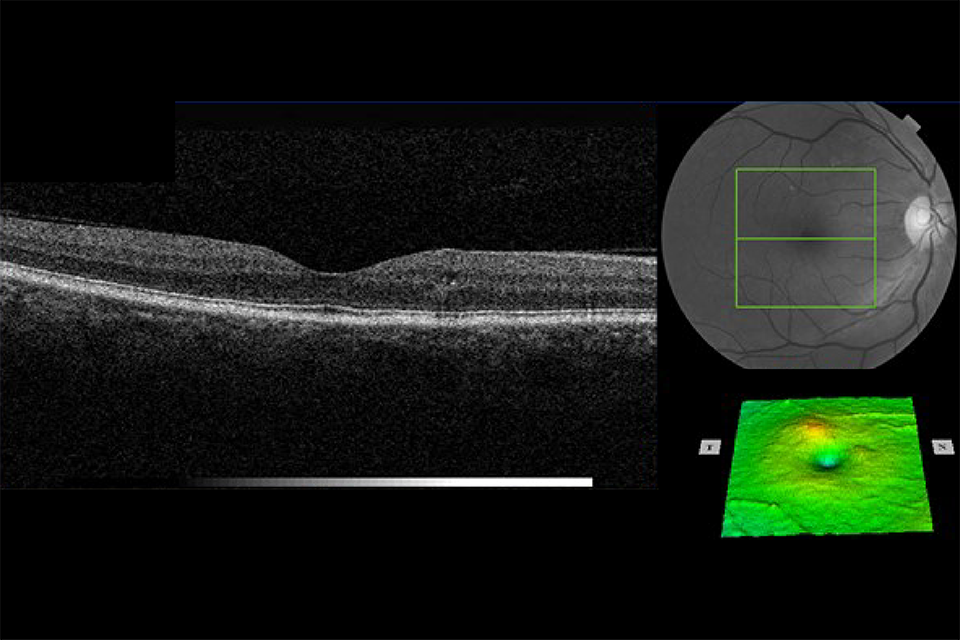
Example 7 R1M1 and OCT positive
Example 7 has an area of retinal thickening greater than 1/2 disc area, the edge of which is within 1 DD of the central fovea. It has:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1
- intraretinal cysts
- no change in foveal contour
- retinal thickening (more than 1/2 DA) the edge of which is within 1 DD of the central fovea
Outcome: referral to HES (unless extenuating circumstances requested by clinical lead).
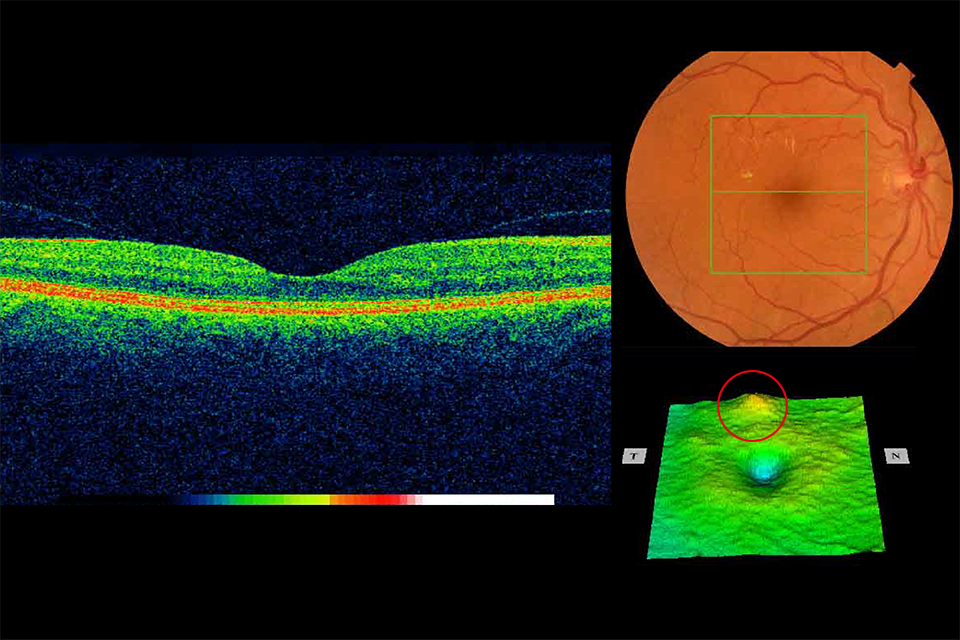
Example 8 R1M1 and OCT positive. No change in foveal contour but thickening more than 1 disc area circled in red
Example 8 has an area of retinal thickening greater than 1 disc area within the NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme definition of the macula. It has:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1
- intraretinal cysts
- no change in foveal contour
- retinal thickening (more than 1 DA within the macula)
Outcome: referral to HES (unless extenuating circumstances requested by clinical lead).
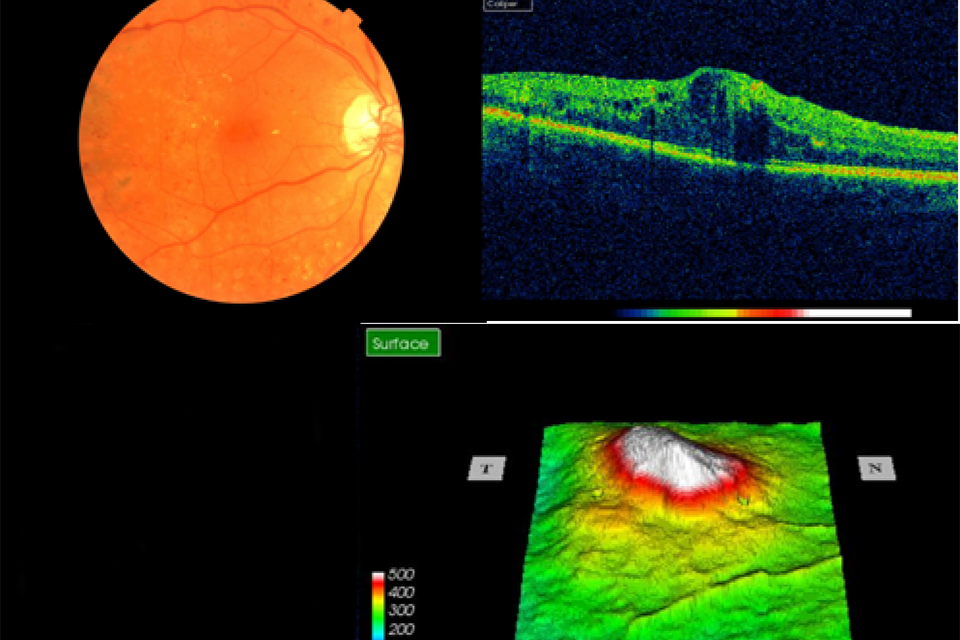
Example 9 R1M1 and OCT positive
Example 9 shows significant central thickening. It has:
- photographic surrogate markers for M1
- intraretinal cysts
- significant change in foveal contour
- significant diffuse retinal thickening more than 400 µm
Outcome: refer to HES soon and within 4 weeks for Anti-VEGF if central subfield thickness more than 400 µm. The referral outcome grader must refer routinely within the software and make a note on the HES referral recommending a 4 week appointment.
