Using the Mail Transfer Agent Strict Transport Security (MTA-STS) protocol in your organisation
Updated 15 March 2021
Mail Transfer Agent Strict Transport Security (MTA-STS) is a protocol which tells services that are sending your organisation email that your domain supports Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 or higher. This protocol makes email less vulnerable to middleperson attacks and allows the receiving email service to enforce encryption, without the risk of delivery failing.
If the sending email service does not support MTA-STS or TLS, the email could still be delivered unencrypted.
As an email administrator, you do not need your provider to support MTA-STS to protect emails sent to your organisation. The sender of the email has to support MTA-STS on outbound email for the protocol to work.
Understanding how MTA-STS works
An MTA-STS policy is a text file published to the internet which contains important details about the protocol. This policy contains the:
-
mode - this can be ‘enforce’, ‘testing’ or ‘none’
-
list of servers in your MX records
-
maximum amount of time the sending service should cache the policy
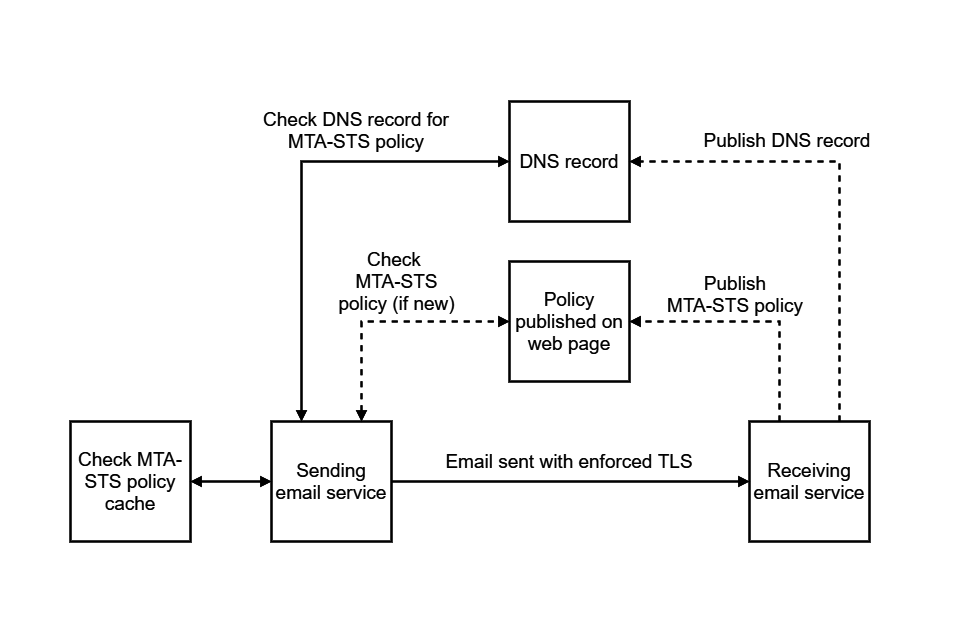
The sending email service will check the Domain Name System (DNS) record of the receiving email service for an MTA-STS policy at _mta-sts.example.gov.uk. The record says if there is an MTA-STS policy and shows the current ID number.
If the sending mail service does not have a cached policy for this domain, or the current ID is newer, the service will automatically download the policy from https://mta-sts.example.gov.uk/.well-known/mta-sts.txt.
Caching the policy protects against any unreliability of the MTA-STS policy hosting infrastructure or DNS. It is safe to leave the policy for a maximum of 6 months. Sending email services will check the policy ID for changes daily.
Sending email to a domain with MTA-STS
When an ‘enforce’ policy is in place for the receiving domain, the sending email service will make sure:
-
an email is sent using TLS1.2 or higher
-
a trusted certificate authority has signed the certificate and it is in date
-
the certificate is valid for the mail server hostname
-
the mail server hostname matches one of the entries in the policy
If any of these are not true, the sending email service will disconnect and try a different server or try again later.
