End User Devices Security Guidance: Windows 10
Published 23 November 2015
1. About this guidance
The End User Devices Security and Configuration Guidance is for Risk Owners and Administrators to understand the risks, security advantages and recommended configuration of Windows 10 within a remote working environment at the OFFICIAL and OFFICIAL SENSITIVE classification. Risk owners are encouraged to read the Risk owners’ summary and Enterprise considerations sections. Administrators and system integrators are encouraged to read the whole document.
This ALPHA guidance has been developed for the first release of Windows 10 Enterprise, and builds on previous guidance for Windows 8.1 Enterprise. The ALPHA release aims to allow a device running Windows 10 to have at least the same security characteristics as one running a previous version of Windows. This guidance will be updated to take advantage of some of the newer features of Windows 10.
This guidance was developed following testing performed on a Windows Hardware Certified device running Windows 10 Enterprise. The device was on the Current Business Branch and managed with Active Directory on Server 2012 R2. This guidance is not applicable to Windows RT or Windows To Go. This guidance has not been tested against the Windows 10 MDM management capability.
It is important to remember that any guidance points given here are just recommendations; none of which are mandatory. They have been suggested as a way of satisfying the 12 security recommendations that mitigate the threat at OFFICIAL. Risk owners and administrators should agree a configuration which balances the business requirements, usability and security of the platform and use this guidance for advice where needed.
2. Risk owners’ summary
When using Windows 10 as part of a remote working scenario, the following architectural choices are recommended to minimise risk:
-
All data should be routed over a secure enterprise VPN to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the traffic, and to allow the devices and data on them to be protected by enterprise protective monitoring solutions.
-
Arbitrary third party application installation by users is not permitted on the device. Applications should be authorised by an administrator and deployed via a trusted mechanism.
-
Most users should use accounts with no administrative privileges. Users that require administrative privileges should use a separate unprivileged account for email and web browsing. It is recommended that local administrator accounts have a unique strong password per device.
When configured in this way, risk owners should be aware of the following technical risks associated with this platform. These technical risks are associated to one of the 12 security principles for end user devices.
| Associated security principle | Explanation of risks |
|---|---|
| Secure boot | Windows 10 can support secure boot, but is dependent on supported and correctly configured hardware |
3. Administrators’ deployment guide
To meet the principles outlined in the End User Devices Security Framework, several recommendations are given in the table below.
3.1 Overview
| Security principle | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Data in transit | Use DirectAccess or the native IKEv2 IPsec VPN configured as per the Windows VPN Security Procedures. If "DirectAccess" is used, follow the CPA customisation guide (available via CESG enquiries) to configure the client. If the native IKEv2 IPSec VPN is used, configure the built-in Windows firewall to block outbound connections when the VPN is not active. The L2TP and IPsec VPNs do not initiate automatically at boot and there is potential for the user to disconnect the VPN at any time. An example firewall profile is provided in the Configuration Settings section which demonstrates how to mitigate this behaviour. If certificates are used for user or machine credentials, it is recommended that Windows Key Attestation is used. Alternatively, the Windows 10 platform allows the use of third party VPN clients. Use a correctly configured CPA Foundation grade client. |
| Data at rest | Use BitLocker with a TPM and 7 character complex Enhanced PIN configured in alignment with the BitLocker configuration settings. Alternatively use an independently assured CPA Foundation Grade Data at Rest encryption product configured in alignment with the security procedures for that product Deploy the BitLocker configuration settings before encryption is started. BitLocker is not Foundation Grade certified. However, CESG has determined that the level of protection it provides is equivalent to Foundation Grade when configured as per this guidance. “Device Encryption” introduced for Connected Standby devices in Windows 10 does not allow the use of a passphrase to unlock the disk and so does not support some of the mandatory requirements expected from assured disk encryption products. BitLocker or an evaluated third party product should be used instead. |
| Authentication | The user implicitly authenticates to the device by decrypting BitLocker on boot. The user then has a secondary strong 9 character password to authenticate them to the platform after boot and when unlocking the device. This password also derives a key which encrypts certificates and other credentials, giving access to enterprise services. After logon, the credentials will be best protected if the user is a member of the Protected Users group on the domain. Windows Hello permits biometric unlock of devices but the strength of its security is difficult to measure. In cases where there is a requirement to use biometric authentication, and the risks of using biometrics as the sole authentication mechanism are understood, Windows Hello can be enabled. User accounts with administrative privileges should use a strong 14 character secondary password to authenticate them to the platform at logon and unlock time. The credentials will be best protected if administrative users are a member of the Protected Users group on the domain and have Authentication Policy Silos applied. Privileged user accounts should only be used on End User Devices or management terminals that are designated for administration. |
| Secure boot | On Windows 10, this requirement is met on a correctly configured platform deployed on Windows Hardware Certified hardware. A UEFI/BIOS password can make it more difficult for an attacker to modify the boot process. With physical access, the boot process can still be compromised. |
| Platform integrity and application sandboxing | This requirement is met by the platform without additional configuration. |
| Application whitelisting | An enterprise configuration can be applied to implement application control (using AppLocker). A recommended sample configuration that only allows Administrator-installed applications to run is provided below. |
| Malicious code detection and prevention | Windows 10 includes Windows Defender and Windows SmartScreen that attempt to detect malicious code for this platform. Cloud sample submission can be disabled. Alternatively, third party anti-malware products are available. The Early Launch Anti-Malware (ELAM) driver provides signature checking for known bad drivers on ELAM compliant systems that are configured to use Secure Boot. A Company Store can be used to distribute user-installable universal apps which should only contain vetted apps. If the public Windows Store is enabled, AppLocker can be used to control which applications a user can install. Content-based attacks can be filtered by scanning capabilities in the enterprise. The Microsoft Enhanced Mitigation Experience Toolkit (EMET) should be used to help prevent vulnerabilities in older software from being successfully exploited. |
| Security policy enforcement | Settings applied through Group Policy cannot be modified by unprivileged users. |
| External interface protection | Interfaces can be configured using group policy. USB removable media can be blocked through Group Policy if required. Direct Memory Access (DMA) is possible from peripherals connected to some external interfaces including FireWire, eSATA, and Thunderbolt unless disabled through group policy as detailed below, or in the UEFI/BIOS. With Windows 10 connected standby devices, part of the hardware compliance mitigates DMA attacks by disallowing these interfaces. |
| Device updates | Windows Update can automatically download and install updates. If the Windows Store is enabled, it should be configured to automatically update Windows Store apps. Windows Update for Business or Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) can optionally be used to monitor and enforce updates of the core platform, system firmware and any Windows applications. |
| Event collection | Event collection can be carried out using Windows Event Forwarding for central event log collection. |
| Incident response | The combination of BitLocker drive encryption and enterprise revocation of user credentials are appropriate for managing this security recommendation. |
3.2 Recommended network architecture
All remote or mobile working scenarios should use a typical remote access architecture based on the Walled Garden Architectural Pattern. The following network diagram describes the recommended architecture for this platform.
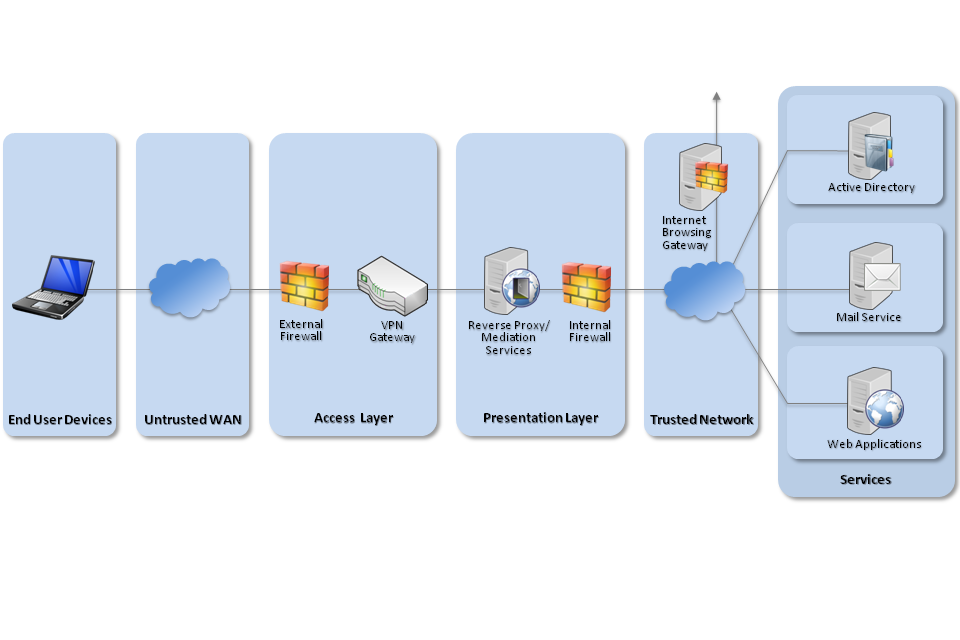
Recommended network architecture for Windows 10 deployments
4. Deployment process
To prepare the enterprise infrastructure:
-
Procure, deploy and configure network components, including an approved IPsec VPN Gateway.
-
Configure Windows Deployment Services (WDS) to deploy the organisations standard desktop build using a clean Windows 10 Enterprise image. For larger deployments include credential management tools such as LAPS and MBAM.
-
Create Group Policies for user and computer groups in accordance with the settings later in this section ensuring that the Microsoft Baseline settings have the lowest precedence when being deployed. It may be necessary to import ADMX files from Windows 10, Windows 8.1 and the SCM draft before they can be edited on Windows Server.
-
Deploy an AppLocker rule set using Group Policy following guidance in Application Whitelisting. A sample configuration that only allows applications that have been installed by an Administrator to run is outlined in the Group Policy settings below.
-
Create Event Forwarding Subscriptions and configure Group Policy to forward at least AppLocker, Application, System and Security logs that have a level of Critical Error or Warning to an event management system as per NSA guidance.
-
Configure user groups according to the principle of least privilege. Where available, configure these users to be in the Protected Users group and apply Restricted Admin and Authentication Policy Silos to privileged users.
5. Provisioning steps
To provision each device to the enterprise infrastructure:
-
Update the system firmware to the latest version available from the vendor. This may be called a UEFI or BIOS update.
-
Configure the system firmware to boot in UEFI mode, enable Secure Boot, disable unused hardware interfaces, check the boot order to prioritise internal storage and set a password to prevent changes.
-
Apply the clean Windows build to the device from the deployment server. This may overwrite the customised version of Windows provided by the device vendor.
-
Deploy the most recent version of EMET (5.5 at the time of writing) and configure it using Group Policy configuration given below.
6. Recommended policies and settings
The following table shows a recommended set of policies that will result in a reasonable balance between technical risk and usability. Organisations are encouraged to adjust these policies in consultation with their risk owners to maximise these devices’ business benefit whilst still ensuring that each of the twelve security principles are addressed. For full details of what each policy controls, see the platform vendor’s documentation.
Settings not listed in this section are either not applicable to this mode or should be chosen according to organisational policy and requirements.
For easy configuration, you can download a zip file containing the custom CESG GPO settings.
6.1 Microsoft baselines
The configuration below builds on the enterprise baselines distributed by Microsoft with the Security Compliance Manager tool. Microsoft has not yet released Windows 10 baselines as part of the tool. The configuration below has been specifically designed to work with the draft Windows 10 baseline configurations. You should use:
- draft SCM Windows 10 – Computer
- draft SCM Windows 10 – User
- draft SCM Windows 10 – BitLocker
- SCM Internet Explorer 11
6.2 User account hardening
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > Network Connections > Require domain users to elevate when setting a network’s location | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Credential User Interface > Do not display the password reveal button | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > OneDrive > Prevent the usage of OneDrive for file storage | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Sync your settings > Do not sync | Enabled Allow users to turn syncing on: Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Search > Allow Cortana | Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Search > Don’t search the web or display web results in Search | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Store > Turn off the Store application | Enabled |
| User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Control Panel > Personalization > Screen saver timeout | 600 seconds |
User authentication should be configured in line with your organisation’s password policy. A suggested interpretation of CESG’s password guidance for Windows 10 is listed below:
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| CN=System > CN=Password Settings Container > CN=Granular Password Settings Users | Precedence: 2 Enforce minimum password length: 9 characters Password must meet complexity requirements: Enabled Enforce lockout policy: 5 attempts Account will be locked out: Until an administrator manually unlocks the account Directly Applies To: Domain Users |
| CN=System > CN=Password Settings Container > CN=Granular Password Settings Administrators | Precedence: 1 Enforce minimum password length: 14 characters Password must meet complexity requirements: Enabled Enforce lockout policy: 5 attempts Account will be locked out: Until an administrator manually unlocks the account Directly Applies To: Domain Admins Protect from accidental deletion: Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Logon > Turn off picture password sign-in | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Components > Microsoft Passport for Work > Use a hardware security device | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Components > Microsoft Passport for Work > Use Microsoft Passport for Work | Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Components > Microsoft Passport for Work > Use biometrics | Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options > Accounts: Block Microsoft accounts | Users can't add or log on with Microsoft accounts |
6.3 System hardening
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Defender > MAPS > Send file samples when further analysis is required | Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Data Collection and Preview Builds > Allow Telemetry | Enabled: 0 - Security |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Error Reporting > Disable Windows Error Reporting | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Update > Configure Automatic Updates | Enabled: 3 - Auto download and notify for install |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Update > Defer Upgrades | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Store > Turn off Automatic Download and Install of updates | Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > App runtime > Block launching Windows Store apps with Windows Runtime API access from hosted content. | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Device Installation > Device Installation Restrictions > Prevent installation of devices that match these device IDs | Enabled:
PCI\CC_0C0A Also apply to matching devices that are already installed: Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Device Installation > Device Installation Restrictions > Prevent installation of drivers matching these device setup classes | Enabled:
d48179be-ec20-11d1-b6b8-00c04fa372a7 Also apply to matching devices that are already installed: Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > Network Isolation > Proxy definitions are authoritative | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > Network Isolation > Subnet definitions are authoritative | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Portable Operating System > Windows To Go Default Startup Options | Allow user trusted root Certificate Authorities (CAs) to be used to validate certificates: Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options > Public Key Policies > Certificate Path Validation Settings > Stores | Disabled |
| Computer Configuration > Preferences > Windows Settings > Registry > Replace > HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ policies\system\ | (DWORD) SafeModeBlockNonAdmins = 1 |
Group Policy can be used to limit user access to removable media such as USB mass storage devices if required by organisational policy. The settings can be found in Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Removable Storage Access.
Group Policy can also be used to fully whitelist all devices or device classes which are allowed to be installed. This could be used to allow, for example, basic peripherals such as mice, keyboards, monitors and network cards, but not allow other devices to be connected and installed. It is important to whitelist enough classes of device to allow a successful boot on a variety of hardware.
Details on how to enable whitelisting of specific devices can be found on MSDN.
6.4 AppLocker configuration
This example set of AppLocker rules implements the principle outlined in Enterprise Considerations below.
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > System Services > Application Identity | Startup Mode: Automatic Action: Start service Startup type: Automatic Log on as: No change |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Enforcement > Executable Rules | Configured: True Enforce Rules |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Executable Rules | Allow Everyone: All files located in the Program Files folder Allow Everyone: All files located in the Windows folder - with exceptions Exception: %SYSTEM32%\catroot2\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\com\dmp\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\FxsTmp\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\drivers\color\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\PRINTERS\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\SERVERS\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Tasks\* Exception: %WINDIR%\debug\* Exception: %WINDIR%\pchealth\ERRORREP\* Exception: %WINDIR%\registration\* Exception: %WINDIR%\tasks\* Exception: %WINDIR%\temp\* Exception: %WINDIR%\tracing\* Exception: cscript.exe 5.8.0.0-* from Microsoft Corporation Exception: wscript.exe 5.8.0.0-* from Microsoft Corporation Allow Administrators: All files |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Enforcement > Windows Installer Rules | Configured: True Enforce Rules |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Windows Installer Rules | Allow Administrators: All Windows Installer files Allow Everyone: %WINDIR%\Installer\* |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Enforcement > Script Rules | Configured: True Enforce Rules |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Script Rules > Enforce rules of this type | Allow Everyone: All Scripts located in the Program Files folder Allow Everyone: All Scripts located in the Windows folder - with exceptions Exception: %SYSTEM32%\catroot2\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\com\dmp\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\FxsTmp\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\drivers\color\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\PRINTERS\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\SERVERS\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Tasks\* Exception: %WINDIR%\debug\* Exception: %WINDIR%\pchealth\ERRORREP\* Exception: %WINDIR%\registration\* Exception: %WINDIR%\tasks\* Exception: %WINDIR%\temp\* Exception: %WINDIR%\tracing\* Allow Administrators: All scripts |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Enforcement > DLL Rules | Configured: True Enforce Rules |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > DLL Rules | Allow Everyone: All DLLs located in the Program Files folder Allow Everyone: All DLLs located in the Windows folder - with exceptions Exception: %SYSTEM32%\catroot2\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\com\dmp\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\FxsTmp\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\drivers\color\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\PRINTERS\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Spool\SERVERS\* Exception: %SYSTEM32%\Tasks\* Exception: %WINDIR%\debug\* Exception: %WINDIR%\pchealth\ERRORREP\* Exception: %WINDIR%\registration\* Exception: %WINDIR%\tasks\* Exception: %WINDIR%\temp\* Exception: %WINDIR%\tracing\* Allow Administrators: All DLLs |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Enforcement > Packaged app Rules | Configured: True Enforce Rules |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Application Control Policies > AppLocker > Packaged app rules | Allow Everyone: All signed packaged apps - with exceptions Exception: Microsoft.Getstarted Exception: Microsoft.MicrosoftOfficeHub Ecveption: Microsoft.SkypeApp Exception: Microsoft.WindowsFeedback |
6.5 BitLocker configuration
BitLocker PIN length should be configured to be in line with CESG’s password guidance. A suggested interpretation is included below. Deployments that include fixed-location workstations may prefer to use BitLocker Network Unlock as an alternative to a PIN.
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption > Operating System Drives > Allow enhanced PINs for startup | Enabled |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption > Operating System Drives > Configure minimum PIN length for startup | Enabled Minimum Characters:7 |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption > Operating System Drives > Enforce drive encryption type on operating system drives | Enabled Select the encryption type: Full encryption |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption > Operating System Drives > Require additional authentication at startup | Enabled Allow BitLocker without a compatible TPM (Requires a password or startup key on a USB flash drive): Unticked Configure TPM startup: Do not allow TPM Configure TPM startup PIN: Allow startup PIN with TPM Configure TPM startup key: Do not allow startup key with TPM Confgure TPM startup key and PIN: Allow startup key and PIN with TPM |
6.6 EMET configuration
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > EMET > Default Action and Mitigation Settings | Enabled Deep Hooks: Enabled Anti Detours: Enabled Banned Functions: Enabled Exploit Action: Stop Program |
| Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > EMET > System DEP | Enabled DEP Setting: Always On |
Group Policy should be used to apply EMET to Enterprise applications which render untrusted data such as those which are Internet facing. The required settings can be found in Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > EMET > Application Configuration.
6.7 Firewall configuration
This firewall configuration is used to enforce the use of an always-on VPN.
You may also need to add rules to allow your VPN client to make outbound connections when the device is in a public or private profile. Sample rules are provided with the CPA configuration guide for Direct Access.
If you need to add firewall exceptions to allow for remote management, they should only be applied to the Domain profile.
| Group Policy | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall Properties > Domain Profile | Firewall State : On (Recommended) Inbound connections : Block (default) Outbound connections : Allow (default) |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall Properties > Domain Profile > Settings > Customize > Apply local firewall rules | No |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall Properties > Private Profile | Firewall State : On (Recommended) Inbound connections : Block (default) Outbound connections : Block |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall Properties > Private Profile > Settings > Customize > Apply local firewall rules | No |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall Properties > Public Profile | Firewall State : On (Recommended) Inbound connections : Block (default) Outbound connections : Block |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall Properties > Public Profile > Settings > Customize > Apply local firewall rules | No |
| Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Outbound Rules | Enabled Allow outbound DHCP General > Action: Allow the connection Programs and Services > Programs > This Program > %SystemRoot%\system32\svchost.exe Allow Programs and Services > Service > Apply to this service > DHCP Client (Dhcp) Advanced > Profiles: Private, Public Protocols and Ports > Local port: UDP 68 Protocols and Ports > Remote port: UDP 67 Allow outbound DNS General > Action: Allow the connection Programs and Services > Programs > This Program > %SystemRoot%\system32\svchost.exe Allow Programs and Services > Service > Apply to this service > DNS Client (Dnscache) Advanced > Profiles: Private, Public Protocols and Ports > Remote port: TCP 53, UDP 53 Allow outbound Kerberos General > Action: Allow the connection Programs and Services > Programs > This Program > %SystemRoot%\system32\lsass.exe Advanced > Profiles: Private, Public Protocols and Ports > Remote port: All TCP and UDP ports Allow outbound LDAP General > Action: Allow the connection Programs and Services > Programs > This Program > All programs that meet the specified conditions Advanced > Profiles: Private, Public Protocols and Ports > Remote port: TCP 389, UDP 389 Allow outbound NCSI Probe General > Action: Allow the connection Programs and Services > Programs > This Program > %SystemRoot%\system32\svchost.exe Allow Programs and Services > Service > Apply to this service > Network Location Awareness (NlaSvc) Advanced > Profiles: Private, Public Protocols and Ports > Remote port: TCP 80 |
6.8 VPN configuration
If using the native IKEv2 IPsec VPN client, it should be configured to negotiate using the following parameters.
| Settings | Value(s) |
|---|---|
| IKE DH Group | 14 (2048-bit) |
| IKE Encryption Algorithm | AES-128 |
| IKE Hash Algorithm | SHA-1 |
| IKE Authentication Method | RSA X.509 |
| IPsec Encryption | AES-128 |
| IPsec Auth | SHA-1 |
| SA Lifetime | 24 Hours |
If using the “DirectAccess” client, it should be configured using the CPA customisation guide which is available via CESG enquiries.
Both these configurations differ slightly from that of other End User Devices (which follow the PRIME and PSN interim profiles) as they are not completely supported by Windows 10. A secondary VPN server or configuration may therefore need to be configured to run in parallel if other devices are being deployed.
7. Enterprise considerations
The following points are in addition to the common enterprise considerations and contain specific issues for Windows 10 deployments.
7.1 Windows 10 feature updates
Microsoft have changed their approach to updating Windows in Windows 10. This change allows the platform to be updated to add major features more regularly, with an anticipated release every four months. Only currently supported releases will receive security patches. The support period varies depending on which servicing model is followed.
CESG recommends adopting the Current Branch for Business servicing model. It gives the option of deferring feature upgrades if time is needed to fix compatibility problems with other enterprise services. Enterprises can run a pilot with a subset of their users and devices on the Current Branch and Insider builds to allow them to identify compatibility issues in advance of the majority of users receiving the same feature updates.
Future updates to this guidance are expected to cover features such as Passport for Work, Device Guard, Credential Guard, Health Attestation and the Business Store.
The Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Branch is designed for devices that never change, such as medical equipment and components in industrial control systems. It should not be deployed on OFFICIAL End User Devices that are used to browse the web or use enterprise productivity software.
7.2 System firmware
Many of the newer security mitigations of Windows require the system to be configured to use UEFI and a TPM. Even if you are not deploying these mitigations at the moment, you should seek to buy Windows Hardware Compliant devices that support TPM 2.0 and UEFI v2.3.1 or higher.
You should ensure that devices are configured to boot from UEFI when initially installing Windows 10 on them even if you choose to not configure some of the features that require it. This will make future version upgrades and adoption of those features easier at a later date.
7.3 Secure boot
The Windows 10 Secure Boot process (on supported and correctly configured hardware) alerts a user when an attempt to subvert the security controls has taken place. It is important that users know how to identify and respond to this alert.
7.4 Application whitelisting
When configuring additional application whitelists for a Windows device, it is important that the following conditions are considered:
-
Users should not be allowed to run programs from areas where they are permitted to write files.
-
Care should be taken to ensure that application updates do not conflict with whitelisting rules.
-
Applications should be reviewed before being approved in the enterprise to ensure they don’t undermine application whitelisting. This is especially important for scripting languages which have their own execution environment.
The suggested AppLocker configuration in this guidance will implement those rules if using software that adheres to the requirements of Microsoft’s Desktop App Certification Program. If the rules do need to be customised, follow Microsoft’s Design Guide to minimise the impact to the operation of the enterprise.
7.5 Universal applications
The configuration given above prevents users from accessing the Windows Store to install applications, but an organisation can still host its own enterprise Company Store to distribute in-house applications to their employees if required.
If the Windows Store is enabled, users should explicitly use their corporate Microsoft ID to sign into the Store app rather than associating their work device with their personal Microsoft ID. AppLocker can be configured to only allow installation of apps that are on an enterprise-configured “allow” list.
7.6 Cloud integration
Windows 10 devices do not need to be associated with a Microsoft ID to operate as required within the enterprise. Users should not enable personal, non-enterprise Microsoft ID (Live ID) accounts on the device as this may allow data to leak through Microsoft cloud services backup and application storage.
However, organisations wishing to use cloud based services such as OneDrive can use the CESG Cloud Security Guidance to help them understand both the benefits and risks of using online services.
7.7 Enterprise software protections
Enterprise software that handles untrusted data downloaded from the Internet through the browser needs additional protections.
Application sandboxing and content rendering controls should be considered essential. For applications such as Microsoft Office, or Adobe Acrobat, the use of their enterprise security controls should be considered. These security controls aim to help protect the end user when processing these potentially malicious files.
Modern web browsers have to process a wide variety of rich content from the Internet – some of which must be considered untrustworthy – as well as providing a trusted platform to run enterprise web apps. It is strongly recommended that organisations read the CESG Web Browser Security Guidance to help them understand the security controls available in the most common web browsers.
Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) can be used to deploy and update Microsoft products but cannot keep third party products up to date unless they have a package in the enterprise system management service.
