Child and Working Tax Credits Statistics: Provisional Awards December 2020 Geographical Supporting Commentary
Published 26 February 2021
1. A National Statistics Publication
National Statistics are produced to high professional standards as set out in the Code of Practice for Official Statistics. They undergo regular quality assurance reviews to ensure that they meet customer needs. They are produced free from any political interference.
The United Kingdom Statistics Authority has designated these statistics as National Statistics, in accordance with the Statistics and Registration Service Act 2007 and signifying compliance with the Code of Practice for Official Statistics.
Designation can be broadly interpreted to mean that the statistics:
- meet identified user needs;
- are well explained and readily accessible;
- are produced according to sound methods;
- are managed impartially and objectively in the public interest;
- are produced to the highest standard, ensuring that data confidentiality has been maintained
Once statistics have been designated as National Statistics it is a statutory requirement that the Code of Practice shall continue to be observed.
For general enquiries about National Statistics, contact the National Statistics Public Enquiry Service on:
Tel: 0845 601 3034 Overseas: +44 (01633) 653 599 Minicom: 01633 812 399 E-mail: info@statistics.gov.uk Fax: 01633 652 747
Letter: Customer Contact Centre, Room 1.101, Government Buildings, Cardiff Road, Newport, South Wales, NP10 8XG.
You can find National Statistics here
2. National Statistics Review
A formal review of our National and Official Statistics publications was held between May and August 2011. Over 130 responses were received from a broad range of users. A report summarising the responses received has been published here.
2.1 HMRC Consultation on Official Statistics
HMRC launched a wide-ranging consultation on a range of statistics on 8th February 2021. This can be found here. This includes changes to a number of tax credits statistics releases including a proposal to reduce the provisional award statistics from twice yearly to annually. An annual publication would be published each summer alongside or as one publication with the Child and Working Tax Credits Finalised Award statistics. Any changes to the tax credit releases will take into account user feedback which we will respond to after the consultation.
3. Introduction
These statistics focus on the number of families benefiting from Child Tax Credit (CTC) and/or Working Tax Credit (WTC) in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland as at 2nd December 2020. This publication presents a breakdown of families by their profile position, age and gender, type of family and family size as well as the number of children in benefiting families, broken down by age. It also includes statistics on families benefiting from each of the different elements of tax credits and provides information on the income used in calculating awards and the frequency of payments.
These statistics are based on a 10% sample of data at the snapshot point and therefore they are estimates and subject to sampling error. They are calculated based on the most recent reported circumstances of each family in the sample. In contrast, the finalised awards statistics publication provides a full, retrospective overview based on every family receiving tax credits in a given financial year and includes details of the tax credits entitlement of those families.
3.1 Impacts of the Covid-19 Pandemic
During 2020, the Covid-19 pandemic has led to some changes in the tax credit system which may have had an impact on these statistics. As part of a number of measures to support the country, the basic element of Working Tax Credit was increased by £1,045 to £3,040 from 6 April 2020 until 5 April 2021. The amount a claimant or household has benefited depends on their circumstances, including their level of household income, how many children they are responsible for or if they are disabled. However claimants will have received an increase of up to £20 each week.
The temporary increase moved many claimants from nil to positive awards at the start of April. At the start of the pandemic, there was also a higher than usual move to Universal Credit (UC) due to unemployment impacts and a reduction in working hours. These impacts have largely offset one another. Policies were also introduced relaxing rules on WTC hours and HMRC automatically renewed tax credit claims for 2019/20 apart from those identified as very high risk. This is likely to have resulted in fewer tax credits terminations than there would have been otherwise.
4. Definitions
4.1 What Are Tax Credits?
Tax credits are a system of financial support for families based on their specific circumstances. The system, introduced in 2003, forms part of wider government policy to provide support to parents returning to work, reduce child poverty and increase financial support for families. The design of the system means that as families’ circumstances change, so does (daily) entitlement to tax credits.
Tax credits are based on household circumstances and can be claimed jointly by couples or by single adults. Entitlement is based on the following factors:
- age
- income
- hours worked
- number and age of children
- childcare costs
- disabilities
For further information about who can claim please refer to the HMRC website
Tax credits are made up of Working Tax Credit and Child Tax Credit, explained below.
4.2 Working Tax Credit (WTC)
Provides in-work support for people on low incomes, with or without children. It is available for in-work support to people who are aged at least 16 and either:
- are single, work 16 or more hours a week and are responsible for a child or young person
- are in a couple and are responsible for a child or young person where their combined weekly working hours are at least 24, with one claimant working at least 16 hours
- work 16 or more hours a week and are receiving or have recently received a qualifying sickness or disability related benefit and have a disability that puts them at a disadvantage of getting a job
- Work 16 or more hours a week and are aged 60 or over
Otherwise, it is available for people who are aged 25 and over who work 30 hours a week or more.
WTC is made up of the following elements:
-
Basic element: which is paid to any working person who meets the basic eligibility conditions.
-
Lone Parent element: for lone parents
-
Second adult element: for couples
-
30 hour element: for individuals who work at least 30 hours a week, couples where one person works at least 30 hours a week or couples who have a child and work a total of 30 hours or more a week between them where one of them works at least 16 hours a week.
-
Disability element: for people who work at least 16 hours a week and who have a disability that puts them at a disadvantage in getting a job and who are receiving or have recently received a qualifying sickness or disability related benefit.
-
Severe disability element: for people who are in receipt of DLA (Highest Rate Care Component), PIP (Enhanced Daily Living Component) or Attendance Allowance at the highest rate.
-
Childcare element: for a single parent who works at least 16 hours a week, or couples who either (i) both work at least 16 hours a week or (ii) one of them work at least 16 hours a week but the other is out of work for being in hospital or in prison and who spends money on a registered or approved childcare provider. The childcare element of WTC can support up to 70% of childcare costs up to certain maximum limits.
Further information on childcare cost support can be found here
4.3 Child Tax Credit (CTC)
Provides income-related support for children and qualifying young people aged 16-19 who are in full time, non-advanced education or approved training into a single tax credit, payable to the main carer. Families can claim CTC whether or not the adults are in work.
CTC is made up of the following elements:
-
Family element: which is the basic element for families responsible for one or more children or qualifying young people. From 6th April 2017, this element is no longer be payable to families where all children were born after this date.
-
Child element: which is paid for each child or qualifying young person the claimant is responsible for. From 6th April 2017, this element is no longer payable in respect of third or subsequent children who were born after this date. Certain exceptions to this rule apply and are set out here.
-
Disability element: for each child or qualifying young person the claimant is responsible for if Disability Living Allowance (DLA) or Personal Independence Payment (PIP) is payable for the child, or if the child is certified as blind or severely sight impaired.
-
Severe disability element: for each child or qualifying young person the claimant is responsible for if DLA (Highest Rate Care Component) or PIP (Enhanced Daily Living Component) is payable for the child.
-
Out-of-work benefit families: some out-of-work families with children do not receive CTC but instead receive the equivalent amount via child and related allowances in Income Support or income-based Jobseeker’s Allowance (IS/JSA). These families are included in the figures, generally together with out-of-work families receiving CTC. The vast majority of these claimants have now moved to tax credits and the remainder will be migrated either to tax credits or Universal Credit.
4.4 Tapering
Tapering is the amount of the award that will be reduced when the household income exceeds a given threshold. For example, the income threshold for claimants receiving WTC only and for combined WTC and CTC claimants is £6,530. After this threshold, the taper rate will be 41%. Tapering reduces WTC first and then CTC for claimants who receive both.
4.5 Child and Working Tax Credit Entitlement
The amount of support an eligible family can receive (known as their entitlement) varies depending on their income and their eligibility for specific tax credit elements. First, a family’s maximum possible entitlement is worked out by adding up all the different elements of CTC and WTC that they are eligible for (described on pages 2-4).
A household’s actual entitlement is then determined by tapering this maximum amount according to different thresholds. As demonstrated within the diagram below, families eligible for the WTC receive the full entitlement until their annual household income reaches £6,530, after which the amount of tax credits they receive is reduced by 41 pence for each £1 they earn beyond this threshold.
If a household is out-of-work and therefore eligible for the CTC only, they will receive the full entitlement until their annual household income reaches £16,385 (2020-21). After this point, the amount of tax credits they receive is again reduced by 41 pence for each additional £1 of income beyond this threshold (note that this is not shown on the diagram below).
In-Work Child and Working Tax Credit Entitlement
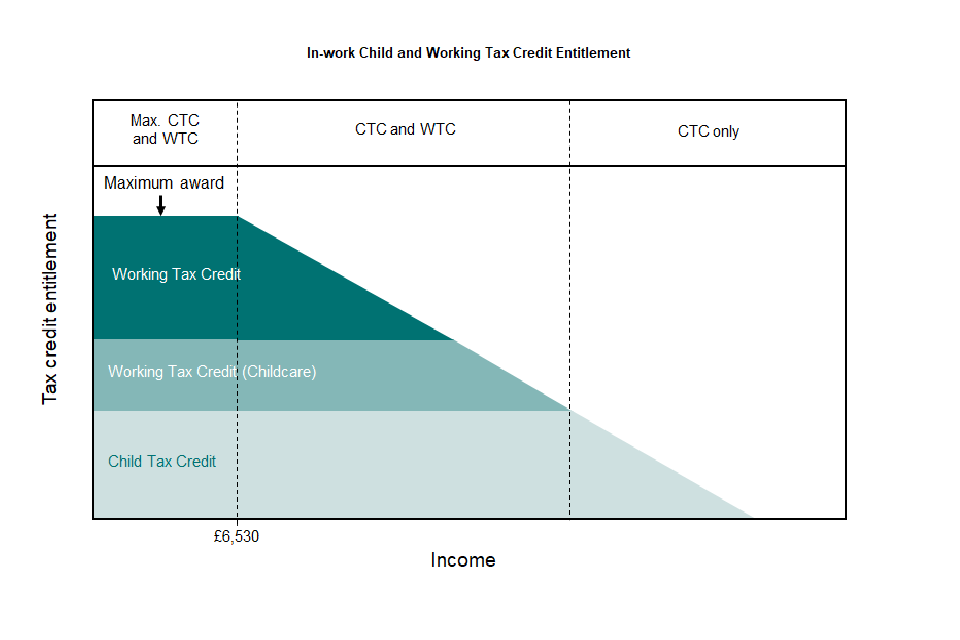
Because of the range of possible eligibilities and interactions between the elements, both the maximum award and the shape of the above award profile will be different for every family with different circumstances.
Tax credits are based on the taxable income of adults within the family. The income used to calculate the award is based on the families’ income from the previous tax year, or on their most recently reported circumstances in-year. Up to £2,500 of any change in annual income between the previous or current year is disregarded in the calculation. A family’s tax credits award is provisional until finalised at the end of the year, when it is checked against their final income for the year. This publication relates to a snapshot of tax credit support based on provisional incomes and other circumstances as reported at the date when the statistics were extracted.
5. About This Publication
5.1 What the Publication Tells Us
The provisional awards are based on a 10% sample of data and are currently published in winter and summer. These statistics are as close to real-time as possible and represent the picture as at the beginning of April and December.
Each release consists of two sets of tables: the main tables and the additional geographical tables. As only a sample of data is used, detailed analysis at the sub-geographical levels is not always possible. The statistics in this release include analysis at the following geographical levels:
- Country and English Region
- Local Authority (LA)
- Westminster Parliamentary Constituency
- Scottish Parliamentary Constituency
The main publication includes a Country and Region summary, with the geographical publication going to a lower level. This series has been produced bi-annually since the introduction of tax credits in April 2003.
5.2 Provisional Awards vs Finalised Awards
It is important to recognise that the finalised awards statistics are not a revision of the provisional statistics. The provisional numbers relate to the caseload position at a snapshot point in time, based on the family circumstances HMRC have been informed of by each family prior to that particular time. The finalised awards relate to the complete retrospective picture for the year, based on a finalised view of family incomes and circumstances. The caseload population will be different between the two publications as a result of HMRC knowing the complete finalised picture of the award.
At the start of the year, the tax credit award will be a provisional award reflecting the reported circumstances as at 6th April (the start of the tax year). Over the course of the year, a family’s circumstances may or may not change. The provisional award is updated each time a family’s circumstances change with the latest set of circumstances and a new provisional award is calculated. It is only at finalisation (usually four to nine months after the end of the tax year) that the family’s circumstances for the whole year are known and a finalised award can be calculated. As a result, the finalised award statistics are not available until around 12 months after the end of the entitlement year in question. Given this lag in availability of data, there is some value in looking at a snapshot of families’ circumstances at any given time, to give some indication of the level of support one might expect to see subsequently at finalisation.
To illustrate the difference, let us look at a family that has one change of circumstance throughout the year, moving from in-work to out-of-work in January of any one year.
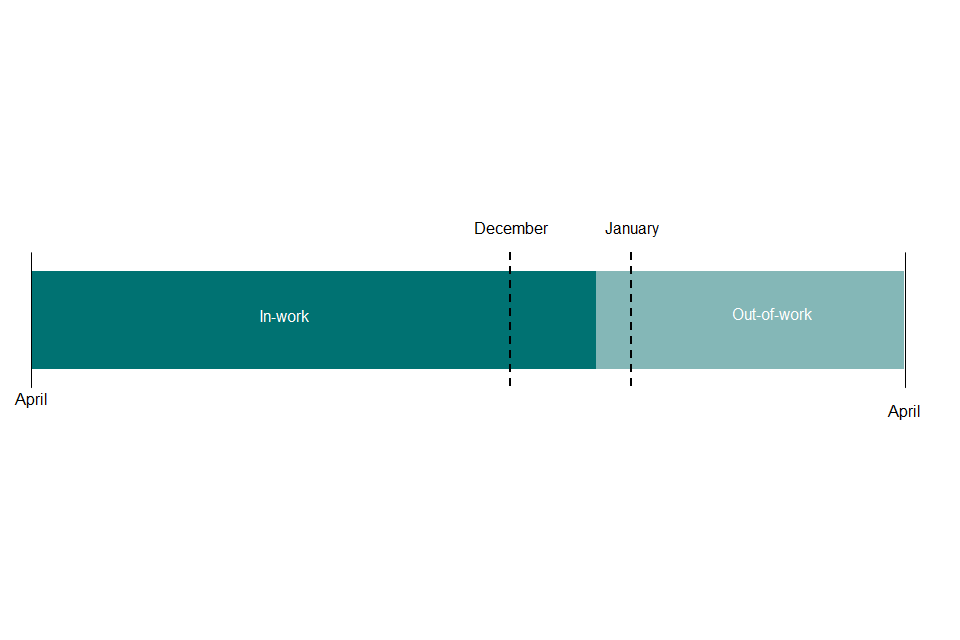
The snapshot data looking at the provisional award in April will model entitlement for the whole year on the basis that the family is in-work for the whole year (since we do not know about the move out-of-work at that time). It is not until finalisation, and thereby in the finalised award data publication, that the family’s entitlement will be modelled on the basis of 9 months in-work and 3 months out-of-work.
Therefore, the figures for provisional awards are more up to date, but are subject to retrospective change. The sizes of these changes can be seen by comparing the data for selected dates in finalised awards with data published earlier on provisional awards at the same time snapshot dates. The provisional award data classify families according to the levels of their entitlement at the reference date, modelled from data on their circumstances and their latest annual incomes reported by that date. The actual amount being received at that date can be lower, due to recovery of earlier overpayments.
5.3 Which Publication Should I Use?
Generally, if you are interested in the final end of year position, use the finalised awards data publication. If you are more concerned with getting the latest up-to-date information that may not align exactly with finalised data further down the line, use the provisional awards data. Using the finalised award data will also mean the figures will align with other published data on tax credits, such as information in HMRC’s Departmental Accounts. The latest finalised award publication can be found here
5.4 What Information Do the Tables Contain?
CTC and WTC are claimed by individuals, or jointly by couples, whether or not they have children (described as “families” in this publication). These tables cover families who had claimed, and were eligible for, CTC (or the equivalent via benefits) or WTC at 2nd December (the “reference date”) and who were recipients at that date.
From April 2007, the tables exclude families whose modelled entitlements are tapered to zero due to their income levels. These families were originally included because they may retrospectively have positive entitlements at finalisation. However, this is no longer likely for the majority of such families. Their numbers have been swelled by families whose youngest children have left full time education, who continue to satisfy the qualifying conditions for WTC, but whose incomes are sufficient to taper the WTC entitlements to zero.
5.5 Recent Policy Changes
In the 2015 Summer Budget, the Government announced that the child element of Child Tax Credit (CTC) would be limited to two children for those born on or after 6 April 2017 unless certain exceptions apply. Prior to 6th April 2017, the child element of CTC was paid for each child or qualifying young person that the claimant (or his or her partner) was responsible for. The change means that any family with two or more existing children do not receive any child element (worth up to £2,830 a year per child in 2019 to 2020) for children born on or after that date, subject to exceptions. The child element of Child Tax Credit continues to be paid for all children born before 6th April 2017.
In addition, any family having their first child born on or after 6th April 2017 do not receive the family element (worth up to £545 a year) of Child Tax Credit. The family element was previously paid to all families. From 6 April 2017, it is only be paid where the claimant is responsible for at least one child or qualifying young person born before 6 April 2017.
For further information, please visit Child Tax Credit Exceptions to the Two Child Limit
Statistics related to this policy can be found here
5.6 Impacts of the Covid-19 Pandemic
In the previous release, it was noted that there would be a further increase of £1,045 per year made to the basic Working Tax Credit element as part of the Government’s response to COVID-19 and that the impact of Covid-19 on these statistics would be seen in the December 2020 data (this publication).
During 2020, the Covid-19 pandemic has led to some changes in the tax credit system which may have had an impact on these statistics. As part of a number of measures to support the country, the basic element of Working Tax Credit was increased by £1,045 to £3,040 from 6 April 2020 until 5 April 2021. The amount a claimant or household has benefited depends on their circumstances, including their level of household income, how many children they are responsible for or if they are disabled. However claimants will have received an increase of up to £20 each week.
The temporary increase moved many claimants from nil to positive awards at the start of April. At the start of the pandemic, there was also a higher than usual move to Universal Credit (UC) due to unemployment impacts and a reduction in working hours. These impacts have largely offset one another. Policies were also introduced relaxing rules on WTC hours and HMRC automatically renewed tax credit claims for 2019/20 apart from those identified as very high risk. This is likely to have resulted in fewer tax credits terminations than there would have been otherwise.
5.7 Universal Credit
Universal Credit (UC) is a payment to help with living costs for those on a low income or out of work. UC was introduced in April 2013 in certain areas of North West England. Since October 2013, it has progressively been rolled out to other areas. Claimants receive a single monthly household payment, paid into a bank account in the same way as a monthly salary and support for housing costs, children and childcare costs are integrated into Universal Credit. Child Tax Credit will be replaced as Universal Credit rolls out. Due to most tax credit recipients now claiming Universal Credit instead (the full roll out of this service has commenced), there are no longer any new tax credit claims (with the exception of those claiming the family premium).
Further information about Universal Credit, including making a claim, is available online here
Statistics related to UC are available online and can be found here
6. Uses of These Statistics and User Engagement
6.1 Uses of These Statistics
The statistics contained in this publication will be of interest for anyone that is looking for the latest possible data on tax credits or detailed up-to-date geographical estimates of the number of families receiving tax credits. Specifically, there are aggregate statistics on the type and level of tax credit support, broken down by categories such as family composition, family income, work status, and geographical area. It may be of interest to academics, think tanks and political parties interested in the twin aims of tax credits - eradicating child poverty and improving work incentives. Equally, it may be of interest to people considering wider questions on government support systems and/or others designing benefit systems. Finally, the geographical analyses might be of interest at the more local level, giving some indication of the level of government support in each region and local authority in the UK.
6.2 User Engagement
Bespoke analysis of tax credits data is possible although there may be a charge depending on the level of complexity and the resources required to produce. If you would like to discuss your requirements, to comment on the current publications, or for further information about the tax credits statistics please use the contact information at the end of this publication, or from the HMRC website
We are committed to improving the official statistics we publish. We want to encourage and promote user engagement, so we can improve our statistical outputs.
We would welcome any views you have by email. We will undertake to review user comments on a quarterly basis and use this information to influence the development of our official statistics. We will summarise and publish user comments at regular intervals.
7. Revision Policy
This policy has been developed in accordance with the UK Statistics Authority Code of Practice for Official Statistics and Her Majesty’s Revenue and Customs Revisions Policy. The UK Statistics Authority Code of Practice can be found here
There are two types of revisions:
Scheduled Revisions This requires explanation of the handling of scheduled revisions due to the receipt of updated information in the case of each statistical publication.
Unscheduled Revisions HMRC aims to avoid the need for unscheduled revisions to publications unless they are absolutely necessary and put systems and processes in place to minimise the number of revisions. Where revisions is necessary due to errors in the statistical process, an explanation along with the nature and extent of revision is also provided. Also, the statistical release and the accompanying tables will be updated and published as soon as is practical.
8. Disclosure Control
In line with HMRC’s Dominance and Disclosure policy, to avoid the possible disclosure of information about individuals, values have been supressed with a “-’’ entry in tables when underlying sample counts are low or zero.
9. Appendix A: Technical Note
9.1 Current Entitlement
There is a single claim form covering both Child and Working Tax Credit, and entitlement is calculated jointly. Awards run to the end of the tax year, and are based on the element values, thresholds, etc. shown at Appendix B.
An annual award is calculated by summing the various elements to which the family is entitled. Unless the family is receiving Income Support, income-based Jobseeker’s Allowance, income-based Employment and Support Allowance or Pension Credit (Guarantee Credit), this sum is reduced if the family’s annual income (see below) exceeds the relevant income threshold. The reduction is 41 per cent of the excess over the threshold.
For 2020 to 2021 awards, the initial calculation of a family’s entitlement is based on its relevant income in 2019 to 2020, which is reported for the final calculation of the 2019 to 2020 award or on the claim form. Relevant income comprises gross annual taxable income from social security benefits (except pensions) and from employment or self-employment, less pension contributions; plus annual income from savings, property, state and private pensions and other sources (but excluding maintenance) in excess of £300. For claims by couples, entitlement is based on their joint annual income.
Final entitlement for 2020 to 2021 is based on 2019 to 2020 income if that is more than £2,500 lower than the income in 2019 to 2020, or exceeds it by more than £2,500. However, the first £2,500 of a fall in income or the first £2,500 rise in income in 2020 to 2021 is disregarded in calculating the tax credit due for that year. The family can report an estimate of its income in 2020 to 2021 at any time, and the award will be recalculated using this income. After the end of the year, the award is finalised when the 2020 to 2021 income is known.
9.2 Change of Circumstances
A family’s circumstances (such as number of children, hours worked, childcare costs, and disabilities) can change within the year. To calculate the annual award, the year is then split into the periods between which the family’s circumstances changed. Entitlement is calculated for each period, based on the annual values shown in Appendix B but scaled down to the number of days in the period. The rate of entitlement attributed to each case for this publication is that for the period spanning the reference date.
9.3 Data Sources
The estimates in the tables for in-work families are based on data from a random sample of families with awards at the reference date, extracted from the tax credits computer system on that date.
The estimates for out-of-work families with children are based on data at 2nd December 2020. The out-of-work families receiving their child support via DWP are based on scans of the benefits systems. These identified all families with children receiving benefits at August 2008. The estimates are restricted to families that had qualifying children in Child Benefit awards at November 2020 and were not claiming tax credits at 2nd December 2020. Figures are subsequently calibrated to total estimates of the population made by the Department for Work and Pensions. The out-of-work families’ claimants’ size in Table 2.1 is the combination of estimate for CTC equivalent paid by DWP plus the estimate for out-of- work families receiving CTC at the extraction date based on a random sample from the HMRC core system taken at that date.
As at 2nd December 2020, families receiving equivalent support through DWP benefits account for just over 1% of the total number of out-of-work families benefiting from tax credits. Weights were given to the sample to gross the total to derive the estimates. Details of weighting is provided in Appendix B.
10. Appendix B: Sampling Method and Sampling Error
The tables are based on a random sample of families receiving CTC or WTC at the reference date. The sample comprises 10 per cent of such single adults (with or without children) and 20 per cent of such couples. Each figure in the tables is derived by weighting the relevant sample cases by the inverses of these sampling fractions . The figures in the tables are, therefore, estimates, but we know how accurate they are.
For example, suppose that there are 100,000 couples with a characteristic. This number is not known, and we are to estimate it via the sample. Each couple is sampled with a chance of 0.2. Statistical theory says that there is a 95 per cent chance that the number sampled will lie between 19,752 and 20,248, and that the resulting estimate will lie between 98,760 and 101,240. At least approximately, then, where an estimate of 100,000 is derived from the sample, the true figure lies between these figures, with a 95 per cent probability. That is, the “95 per cent confidence interval” for the estimate is the estimate itself plus or minus 1,240.
The width of the confidence interval varies with the size of the estimate and the sampling fraction, as shown in the table below. For estimates that comprise a mixture of couples and single adults, the figures will lie between the two sets shown, according to the mix.

Sampling uncertainty: As the figures are based on a sample, therefore they are subject to sampling uncertainty. Figures based on too small a number of cases are shown as “-“
11. Appendix C: Annual Entitlement (£) by Tax Credit Elements and Threshold
| 2008-09 | 2009-10 | 2010-11 | 2011-12 | 2012-13 | 2013-14 | 2014-15 | 2015-16 | 2016-17 | 2017-18 | 2018-19 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Child Tax Credit | |||||||||||
| Family element | 545 | 545 | 545 | 545 | 545 | 545 | 545 | 545 | 545 | 545 | 545 |
| Family element, baby addition [footnote 1] | 545 | 545 | 545 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Child element [footnote 2] | 2,085 | 2,235 | 2,300 | 2,555 | 2,690 | 2,720 | 2,750 | 2,780 | 2,780 | 2,780 | 2,780 |
| Disabled child additional element [footnote 3] | 2,540 | 2,670 | 2,715 | 2,800 | 2,950 | 3,015 | 3,100 | 3,140 | 3,140 | 3,175 | 3,275 |
| Severely disabled child element [footnote 4] | 1,020 | 1,075 | 1,095 | 1,130 | 1,190 | 1,220 | 1,255 | 1,275 | 1,275 | 1,290 | 1,325 |
| Working Tax Credit | |||||||||||
| Basic element | 1,800 | 1,890 | 1,920 | 1,920 | 1,920 | 1,920 | 1,940 | 1,960 | 1,960 | 1,960 | 1,960 |
| Couples and lone parent element | 1,770 | 1,860 | 1,890 | 1,950 | 1,950 | 1,970 | 1,990 | 2,010 | 2,010 | 2,010 | 2,010 |
| 30 hour element [footnote 5] | 735 | 775 | 790 | 790 | 790 | 790 | 800 | 810 | 810 | 810 | 810 |
| Disabled worker element | 2,405 | 2,530 | 2,570 | 2,650 | 2,790 | 2,855 | 2,935 | 2,970 | 2,970 | 3,000 | 3,090 |
| Severely disabled adult element | 1,020 | 1,075 | 1,095 | 1,130 | 1,190 | 1,220 | 1,255 | 1,275 | 1,275 | 1,290 | 1,330 |
| 50+ return to work payment:16 but less than 30 hours per week [footnote 6] | 1,235 | 1,300 | 1,320 | 1,365 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 50+ return to work payment: at least 30 hours per week | 1,840 | 1,935 | 1,965 | 2,030 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Childcare element: Maximum eligible costs allowed (£ per week) | |||||||||||
| Eligible costs incurred for 1 child | 175 | 175 | 175 | 175 | 175 | 175 | 175 | 175 | 175 | 175 | 175 |
| Eligible costs incurred for 2+ children | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Percentage of eligible costs covered | 80% | 80% | 80% | 70% | 70% | 70% | 70% | 70% | 70% | 70% | 70% |
| Common features | |||||||||||
| First income threshold [footnote 7] | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 | 6,420 |
| First withdrawal rate | 39% | 39% | 39% | 41% | 41% | 41% | 41% | 41% | 41% | 41% | 41% |
| Second income threshold [footnote 8] | 50,000 | 50,000 | 50,000 | 40,000 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Second withdrawal rate | 1 in 15 | 1 in 15 | 1 in 15 | 41% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| First income threshold for those entitled to Child Tax Credit only [footnote 9] | 15,575 | 16,040 | 16,190 | 15,860 | 15,860 | 15,910 | 16,010 | 16,105 | 16,105 | 16,105 | 16,105 |
| Income increase disregard [footnote 10] | 25,000 | 25,000 | 25,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 5,000 | 5,000 | 5,000 | 2,500 | 2,500 | 2,500 |
| Income fall disregard [footnote 10] | - | - | - | - | 2,500 | 2,500 | 2,500 | 2,500 | 2,500 | 2,500 | 2,500 |
| Minimum award payable | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 |
-
Payable to families for any period during which they have one or more children aged under one. Abolished 6 April 2011. ↩
-
Payable for each child up to 31 August after their 16th birthday, and for each young person for any period in which they are aged under 20 (under 19 to 2005-06) and in full-time non-advanced education, or under 19 and in their first 20 weeks of registration with the Careers service or Connexions. ↩
-
Payable in addition to the child element for each disabled child. ↩
-
Payable in addition to the disabled child element for each severely disabled child. ↩
-
Payable for any period during which normal hours worked (for a couple, summed over the two partners) is at least 30 per week. ↩
-
Payable for each qualifying adult for the first 12 months following a return to work. Abolished 6 April 2012. ↩
-
Income is net of pension contributions, and excludes Child Benefit, Housing benefit, Council tax benefit, maintenance and the first £300 of family income other than from work or benefits. The award is reduced by the excess of income over the first threshold, multiplied by the first withdrawal rate. ↩
-
For those entitled to the Child Tax Credit, the award is reduced only down to the family element, plus the baby addition where relevant, less the excess of income over the second threshold multiplied by the second withdrawal rate. Abolished effective 6 April 2012. ↩
-
Those also receiving Income Support, income-based Jobseeker’s Allowance or Pension Credit are passported to maximum CTC with no tapering. ↩
-
Introduced from 6 April 2012, this drop in income is disregarded in the calculation of Tax Credit awards. ↩ ↩2
