DCMS Sectors Economic Estimates 2020: Trade headline release
Updated 24 May 2024
1. Headline findings
Released: March 2022
This release provides estimates for the following measures for 2020:
- estimates of exports and imports of goods in DCMS Sectors [footnote 1]
- estimates of exports and imports of services by businesses in DCMS Sectors [footnote 2]
- exports and imports of tourism where exports are defined as spending on goods and services by overseas visitors to the UK and imports are defined as spending by UK visitors overseas.
Estimates of trade in services and trade in goods are not comparable on any basis as they use different data sources and different definitions as to what constitutes an import or an export.
Readers should note that unlike previous years, there are no breakdowns of trade in tourism by world regions or individual countries. We have presented only the headline figures for trade in tourism as published by the Office for National Statistics. This is due to the underlying data source, the International Passenger Survey being suspended from 16 March 2020 to January 2021 as a result of the pandemic.
1.1 Trade in Goods
Trade in DCMS Sector goods in 2020 (current prices) is estimated as:
- £48.6 billion of goods imports, 9.8% of total UK goods imports
- £22.1 billion of goods exports, 7.1% of total UK goods exports
Imports of DCMS sector goods have been consistently higher than exports between 2015 and 2020 (the years of which data are available). This is consistent with the wider UK economy (the UK is a net importer of goods[footnote 3]).
Of the years for which data are available (2015 to 2020), 2020 was the first year in which the value of DCMS sector goods traded in current prices was substantially lower than in the previous year. For imports, this is in line with a UK-wide decrease in the value (in current prices) of goods imports between 2019 and 2020. DCMS sector goods exports saw a proportionally much larger decrease between 2019 and 2020 in value compared to the UK economy as a whole.
The proportion of total UK trade in goods accounted for by goods in DCMS sectors has decreased between 2015 and 2020 for both imports (11.4% to 9.8%) and exports (9.2% to 7.1%) (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Trade in DCMS Sector (excl. Tourism and Civil Society) goods, as a percentage of the UK total: 2015 to 2020

1.2 Trade in services
Trade in services by businesses in DCMS Sectors in 2020 (current prices) is estimated as:
- £40.4 billion of service imports, 25.3% of total UK service imports
- £67.2 billion of service exports, 23.0% of total UK service exports
Exports of services by businesses in DCMS sectors have consistently been higher than imports of services between 2015 and 2020 (Figure 2). This is consistent with the wider UK economy (the UK is a net exporter of services [footnote 4]).
The value of DCMS sector services traded in current prices increased year on year between 2015 and 2020. In contrast, the value of services traded by the UK (in current prices) increased year on year between 2015 and 2019 but fell in 2020.
2020 was the first year (of those for which data are available) that trade by DCMS sector businesses accounted for a larger proportion of UK total service imports than of UK total service exports. This was because UK service imports fell faster than service exports between 2019 and 2020.
The proportion of total UK trade in service accounted for by businesses in DCMS sectors has increased between 2015 and 2020 for both imports (15.0% to 25.3%) and exports (16.9% to 23.0%).
Figure 2: Trade in DCMS Sector (excl. Tourism and Civil Society) services, as a percentage of the UK total: 2015 to 2020

1.3 Trade in Tourism
Tourism imports:
- In 2020, Tourism imports (spend on goods and services by UK visitors overseas) was £13.8 billion (current prices), down from £62.3 billion in 2019.
Tourism exports:
- In 2020, Tourism exports (spend on goods and services by overseas visitors to the UK) was £6.2 billion (current prices), down from £28.4 billion in 2019.
The data source for estimates of trade in Tourism, the International Passenger Survey, was suspended from 16 March 2020 to January 2021 as a result of the pandemic. There are therefore no breakdowns available by world regions or individual countries, and no additional reporting of trade in tourism estimates in this report.
2. Introduction
The DCMS Sectors covered in this release are:
- Creative Industries
- Cultural Sector
- Digital sector
- Gambling (services only)
- Sport
- Telecoms (services only)
- Tourism (covered on a separate basis to the other sectors)
Estimates of trade in services and trade in goods are based on different data sources and are derived using different definitions as to what constitutes an import or an export. They are two separate statistics and cannot be added together or directly compared on any basis (sector or individual country). See data sources section for more information.
This release includes figures up to and including 2020, i.e. these estimates are affected by EU-Exit and the COVID-19 pandemic. Caution is advised when making year on year comparisons of trade in goods or services due to the combined effects of the national and international lockdown restrictions as a result of the pandemic, EU-Exit uncertainty and border disruptions which contributed to the volatility in UK goods and services trade [footnote 5]. See Annex A for a timeline of events and pieces of legislation that occurred between 2015 and 2020 relevant to the movements of goods and people. 2015 is the earliest year for which data is available that allows for reasonable comparison at country level with 2020 data.
Estimates are given in current prices and have not been adjusted for inflation. Year on year increases are therefore likely to be higher than the ‘real’ (inflation-adjusted) value. Changes over time are therefore reported here as changes in the proportion of total UK imports and exports.
Unscheduled revisions have been made to the 2019 exports of goods data as a result of corrections applied to the Overseas Trade in Goods statistics 2015 to 2019 by HMRC. Pre-2019 trade in goods data remain unchanged. Further information on these corrections can be found on the UK Trade Info website.
3. Trade in Goods
Estimates of trade in goods are calculated on a “cross-border” measure of trade; a good is recorded as an export or import when it physically leaves or enters the economic territory of a country. Due to the different definitions and calculations, estimates of trade in goods are not comparable on any basis to the estimates of trade in services. See Data Sources section for further information.
3.1 Trade by DCMS Sectors
In 2020, the value of goods imported by DCMS Sectors exceeded the value of goods exported by £26.5 billion. This was predominantly due to the Digital sector (Figure 3), particularly imports of goods in the ‘Manufacturing of electronics and computers’ sub-sector. DCMS Sectors are not mutually exclusive; industries may contribute to and be classified as more than one sector. For more information, see the DCMS Sector overlaps in Annex B.
FIGURE 3: The net balance of trade* in goods by DCMS Sector, current prices, 2020, UK (£ billions)
| DCMS Sectors | -26.5 |
| Digital Sector | -26.6 |
| Creative Industries | 1.1 |
| Culture Sector | 0.2 |
| Sport Sector | -0.2 |
*A negative net trade balance indicates that the value of goods imported is higher than the value of goods exported.
The value of goods traded by each DCMS Sector is presented below, in current prices.
Creative Industries
In 2020, trade in Creative Industry goods was estimated as:
- £7.8 billion goods imports (1.6% of UK goods imports, down from 2.1% in 2019).
- £8.9 billion goods exports (2.9% of UK goods exports, down from 3.8% in 2019)
Culture Sector
In 2020, trade in Cultural Sector goods was estimated as:
- £6.5 billion goods imports (1.3% of UK goods imports, down from 1.8% in 2019).
- £6.6 billion goods exports (2.1% of UK goods exports, down from 3.1% in 2019),
Digital Sector
In 2020, trade in Digital Sector goods was estimated as:
- £41.4 billion goods imports (8.3% of UK goods imports, up from 7.9% in 2019)
- £14.8 billion goods exports (4.8% of UK goods exports, unchanged from 2019)
Sport Sector
In 2020, trade in Sport Sector goods was estimated as:
- £1.4 billion goods imports (0.3% of UK goods imports, up from 0.2% in 2019).
- £1.2 billion goods exports (0.4% of UK goods exports, down from 0.6% in 2019),
3.2 Trade with European Union (EU) and non-EU countries
This section summarises the trends in DCMS Sector goods trade with the EU and non-EU countries. The EU is a large market for the UK, [footnote 6] [footnote 7] ; trade with the EU accounted for 46.7% of total UK goods imports and 47.9% of total UK goods exports in 2020. Imports of goods
Imports of goods
Less than half of DCMS sector goods were imported from EU countries between 2015 and 2020 (Figure 4). Imports of DCMS sector goods from EU countries decreased as a proportion of total trade between 2015 (44.1%) and 2020 (39.2%). The proportion of DCMS sector goods imported from non-EU countries has increased accordingly over the same time period (2015: 55.9%, 2020: 60.8%).
Total UK goods imports from EU countries also decreased as a proportion of total goods imports between 2015 (54.6%) and 2020 (47.5%). The proportion of UK goods imports from non-EU countries has increased accordingly over the same time period (2015: 45.4%, 2020: 52.5%).
FIGURE 4: The proportion of total goods imports from EU countries by DCMS Sectors and the UK, 2015 to 2020.

Exports of goods
Less than half of DCMS sector goods were exported to EU countries between 2015 and 2020 (Figure 5). Exports of DCMS sector goods to EU countries have increased as a proportion of total trade between 2015 (36.9%) and 2020 (48.7%), with a small decrease in 2017. The proportion of DCMS sector goods exported to non-EU countries has decreased accordingly over the same time period (2015: 63.1%, 2020: 51.3%).
Total UK goods exports to EU countries increased as a proportion of UK total goods trade between 2015 (44.6%) and 2020 (47.8%). The proportion of goods exported to non-EU countries by the UK has fallen accordingly between 2015 (55.4%) and 2020 (52.2%).
FIGURE 5: The proportion of total goods exports to EU countries by DCMS Sectors and the UK, 2015 to 2020.

3.3 Trade with individual countries
This section summarises trade in DCMS sector goods by partner country in 2020 (Figure 6).
Imports of goods
- China (£15.1 billion) was the largest source for DCMS sector goods imports to the UK in 2020, followed by the Netherlands (£7.0 billion).
- In contrast, Germany (£57.1 billion) was the largest source for goods imports across the wider UK economy, followed by China (£53.4 billion) [footnote 2]
- For all of the top five partner countries the Digital Sector was the largest category of DCMS sector goods imports.
Exports of goods
- The USA (£3.7 billion) was the largest market for DCMS sector goods exports in 2020, followed by Ireland (£2.3 billion).
- The USA (£44.7 billion) was also the largest export partner country for goods across the wider UK economy, followed by Germany (£32.6 billion) [footnote 2]
- For the USA and Switzerland, Creative Industries was the largest category of DCMS sector goods exports. The Digital Sector was the largest category of DCMS Sector goods exports for Ireland, Germany and France.
FIGURE 6: the top 5 countries that the UK’s DCMS Sector businesses imported the most goods from and exported the most goods to in 2020

4. Trade in Services
Estimates of trade in services are classified by the business involved in the trade and not the service provided. They are calculated on a change of ownership (balance of payments) measure of trade - if trade moves across land borders but remains under the same ownership this is not counted as trade. Estimates of trade in services are not comparable on any basis to the estimates of trade in goods. See data sources section for further information.
4.1 Trade by businesses in DCMS Sectors
This section summarises the trade in services by businesses in DCMS Sectors in 2020 by individual sector.
In 2020, the value of services exported by businesses in DCMS sectors exceeded the value of services imported by £26.8 billion, predominantly due to businesses in the Digital Sector and the Creative Industries (Figure 7). Exports of services in both sectors are driven by businesses in the ‘Computer programming, consultancy and related activities’, and the ‘IT software and Computer Services’. DCMS sectors are not mutually exclusive; industries may contribute to and be classified as more than one sector. See DCMS Sector overlaps in Annex B.
FIGURE 7: The net balance of trade* in services by businesses in each DCMS Sector, current prices, 2020, UK (£ billions)
| DCMS Sectors | 26.8 |
| Digital Sector | 21.4 |
| Creative Industries | 17.8 |
| Cultural Sector | 4.2 |
| Sport Sector | 2.3 |
| Telecoms Sector | 1.6 |
| Gambling Sector | -0.1 |
*A positive net trade balance indicates that the value of services exported is higher than the value of services imported.
The value of services traded by businesses in each DCMS Sector is presented below in current prices.
Creative Industries
In 2020, trade in services by businesses in the Creative Industries was estimated as: * £23.6 billion service imports (14.8% of UK service imports, up from 10.1% in 2019). * £41.4 billion service exports (14.2% of UK service exports, up from 11.9% in 2019),
Culture Sector
In 2020, trade in services by businesses in the Cultural Sector was estimated as:
- £4.5 billion service imports (2.8% of UK service imports, up from 2.5% in 2019).
- £8.7 billion service exports (3.0% of UK service exports, down from 3.3% in 2019),
Digital Sector
In 2020, trade in services by businesses in the Digital Sector was estimated as:
- £34.1 billion service imports (21.4% of UK service imports, up from 15.4% in 2019).
- £55.5 billion service exports (19.0% of UK service exports, up from 16.3% in 2019).
Gambling Sector
In 2020, trade in services by businesses in the Gambling Sector was estimated as:
- £0.1 billion service imports (0.1% of UK service imports, unchanged from 2019).
Although the Gambling Sector is included in the DCMS Sector exports of services total, we have not reported the value of services exported by the Gambling Sector separately. This is because the aggregated exports of services data for Gambling failed disclosure checks. These are tests that we apply to the data to make sure that respondents to the survey cannot be identified from the results.
Sport Sector
In 2020, trade in services by businesses in the Sport Sector was estimated as:
- £1.7 billion service imports (1.1% of UK service imports, up from 0.5% in 2019).
- £4.0 billion service exports (1.4% of UK service exports, up from 1.2% in 2019).
Telecoms Sector
In 2020, trade in services by businesses in the Telecoms sector (which is wholly within the Digital sector) was estimated as:
- £4.6 billion service imports (2.9% of UK service imports, up from 2.0% in 2019).
- £6.2 billion service exports (2.1% of UK service exports, up from 1.7% in 2019).
4.2 Trade with the European Union (EU) and non-European Union (non-EU) countries
This section summarises trade in services by businesses in DCMS Sectors with EU and Non-EU countries. The EU is a large market for the UK [footnote 6] [footnote 7], trade with the EU accounted for 42.7% of total UK services imports and 35.8% of total UK services exports in 2020.
Imports of services
Service imports by businesses in DCMS sectors from EU countries grew more slowly than imports from non-EU countries, leading to a decrease in the proportion of total imports between 2015 (47.7%) and 2020 (45.0%). Over the same period, the proportion of services imported by businesses in DCMS sectors from non-EU countries increased between 2015 (52.3%) and 2020 (55.0%).
The proportion of UK service imports which were from EU countries fell from 49.6% in 2015 to 42.0% in 2020. The proportion of services imported by UK businesses from non-EU countries increased accordingly from 50.4% in 2015 to 58.0% in 2020.
FIGURE 8: The proportion of total services imported from EU countries by businesses in DCMS Sectors and the UK, 2015 to 2020

Exports of services
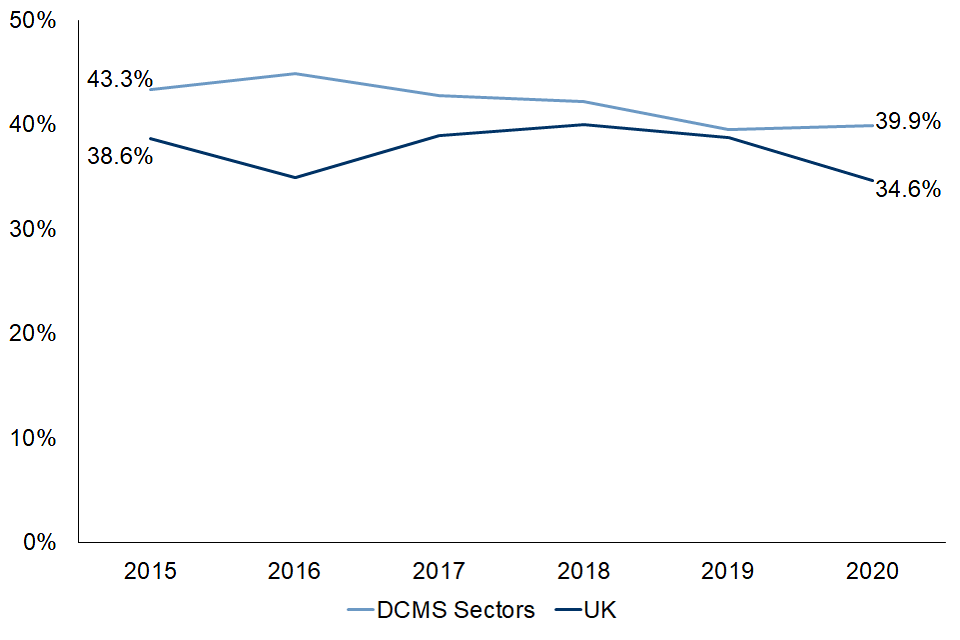
Service exports by businesses in DCMS sectors to EU countries fell as a proportion of total DCMS sector service exports from 43.3% in 2015 to 39.9% in 2020. Over the same period the proportion of services exported to non-EU countries by businesses in DCMS sectors increased between 2015 (56.7%) and 2020 (60.1%). This reflects a relative lack of growth in the value (in current prices) of exports to the EU, particularly between 2018 and 2020.
Total UK exports of services to EU countries fell from 38.6% of total UK service exports in 2015 to 34.6% in 2020. Over the same period, the proportion of services exported to non-EU countries by businesses in the UK economy increased between 2015 (60.6%) and 2020 (64.2%).
FIGURE 9: The proportion of total services exported to EU countries by businesses in DCMS sectors and the UK, 2015 to 2020
4.3 Trade with other countries
This section summarises trade in services by businesses in DCMS sectors by partner country in 2020 (Figure 10).
Imports of services
- The USA (£10.8 billion) was the largest market for services imported by businesses in DCMS sectors in 2020, followed by Ireland (£4.7 billion).
- The USA (£37.5 billion) was also the largest source of services imported by businesses in the wider UK economy, followed by France (£10.8 billion).
- For all the top 5 countries, businesses in the Digital Sector were the largest source for services imported by businesses in DCMS sectors.
Exports of services
- The USA (£20.3 billion) was the largest market for services exported by businesses in DCMS sectors in 2020, followed by Ireland (£4.7 billion).
- Similarly, the USA (£80.1 billion) was the largest market for services exported by businesses in the wider UK economy, followed by Ireland (£17.1 billion).
- For all the top five partner countries, businesses in the Digital Sector were the largest source for services exported by businesses in DCMS Sectors.
FIGURE 10: the top 5 countries that the UK’s DCMS Sector businesses imported services from and exported services to in 2020

5. Trade in Tourism
Unlike previous years, there are no breakdowns available by world regions of individual countries. This is because the underlying data source, the International Passenger Survey, was suspended from 16 March 2020 to January 2021 as a result of the pandemic. The headline figures can be found in Chapter 1 and on the Overseas travel and tourism: 2020 ONS publication page.
6. Data sources
6.1 Trade in goods
Data on trade in goods are collected from HMRC’s Intrastat survey (for EU trade) and customs import and export entries (for non-EU trade), which record the movement (for trade purposes) of goods across international borders. As such, the data are gathered under the cross-border principle of trade.
6.2 Trade in services
The estimates of trade in services are based on data from the ONS International Trade in Services (ITIS) dataset. These data are collected via survey and are gathered under the change of ownership principle of trade. The dataset does not provide full coverage of the economy and excluded sectors include: travel and transport; banking and other financial institutions; higher education; and most activities in the legal professions.
6.3 Trade in Tourism
The estimates of trade in tourism are based on data from the ONS International Passenger Survey (IPS). The survey collects information about passengers entering and leaving the UK and are based on the following definitions;
- Imports of tourism – spending by UK residents on trips abroad
- Exports of tourism – spending by overseas residents during visits to the UK
These figures represent trade in goods and services combined and therefore are not directly comparable with the trade in services or trade in goods estimates presented for all other sectors. Therefore, estimates of imports and exports of Tourism are not presented in the DCMS sector totals.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic the IPS was suspended on 16 March 2020 and resumed in January 2021 [footnote 8]. No IPS data were collected for the period when the survey was not operational. The travel and tourism statistics for April to December 2020 published by ONS are based on administrative sources and modelling. There are therefore no breakdowns available by world regions or individual countries. The only figures available are the headline figures presented in Chapter 1 and the Overseas travel and tourism: 2020 ONS publication page.
Further information on the methodology used to produce the 2020 estimates can be found on the ONS Data sources and quality page.
7. Annex A: Timeline of trade-related events
A timeline of events and pieces of legislation that occurred between 2015 and 2020 and relevant to the movements of goods and people is shown in Table 1 below. We have included events that have been reported as notable by the House of Commons [footnote 9] library and the Office for National Statistics [footnote 10].
TABLE 1: A timeline of trade related events that occurred between 2015 and 2020 and affected the movement of goods and people.
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 23 June 2016 | In a UK referendum held on 23 June 2016, a majority of those who voted chose to leave the European Union [footnote 8]. |
| 29 March 2017 | Article 50 is triggered to commence the two-year countdown to the UK formally leaving the European Union (Brexit) [footnote 8]. |
| March and October 2019 | UK firms stockpile goods ahead of Brexit deadlines in 2019 causing a spike in UK goods imports [footnote 11] |
| 31 January 2020 | The UK officially left the European Union and entered a transition period [footnote 8]. |
| 16 March 2020 | The International Passenger Survey is suspended from operation due to travel restrictions caused by the coronavirus pandemic [footnote 12]. |
| 31 December 2020 | The transition period ended and the United Kingdom left the European Union single market and customs union[footnote 8]. |
8. Annex B: DCMS Sector overlaps
The DCMS sectors are not mutually exclusive; industries may contribute to and be classified as more than one sector. Due to these overlaps, summing over the value of goods or services traded by individual sectors would give a total greater than the actual value.
8.1 Sector overlaps for exports of goods in DCMS Sectors
Figure 11 below shows that the total value of DCMS Sector goods exports (£22.1bn) is not the sum of exports for the individual sectors. The amount of one bar that is vertically above another bar indicates the size of the overlap, for example, the fact that nearly all of the Cultural sector bar is vertically above part of the Creative Industries bar indicates that the majority of the Cultural sector is also within the Creative Industries.
FIGURE 11: Exports of goods of DCMS sectors as a percentage of total UK goods exports (%), 2020
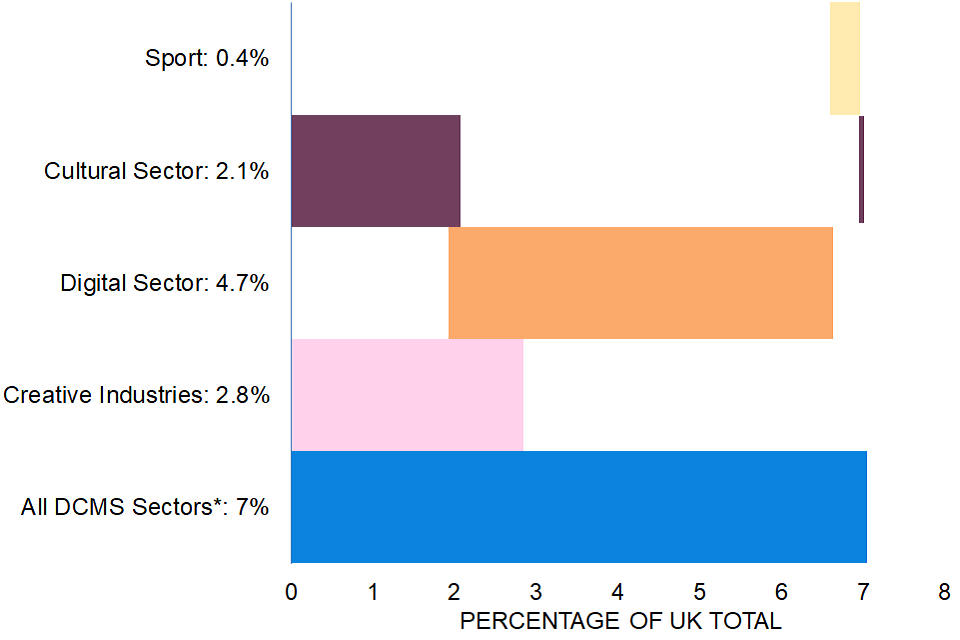
‘All DCMS Sectors’ refers to the Creative Industries and the Digital, Cultural and Sport Sectors.
8.2 Sector overlaps for imports of services in DCMS Sectors
Figure 12 below shows that the total value of services imported by businesses in DCMS sectors (£40.4 billion) is not the sum of imports by businesses in the individual sectors. The amount of one bar that is vertically above another bar indicates the size of the overlap, for example, the fact that nearly all of the Creative Industries bar is vertically below part of the Digital Sector bar indicates that the majority of the businesses in the Creative Industries are also within the Digital Sector.
FIGURE 12: Imports of services of DCMS Sectors as a percentage of total UK service imports (%), 2020
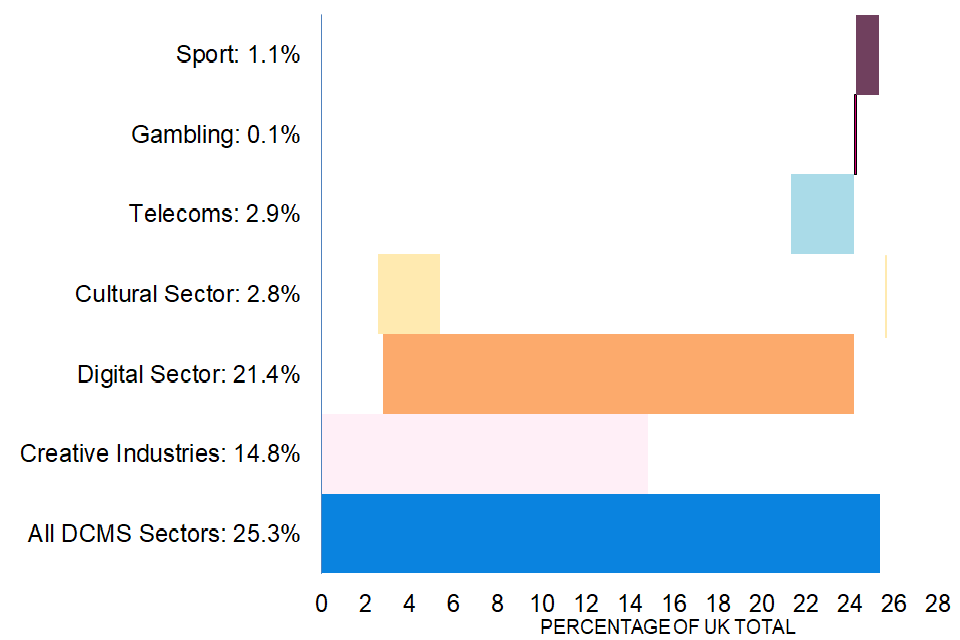
-
The estimates for trade in goods for Civil Society are not covered in this release, as there are no formally recognised Civil Society imports or exports from the data sources available. There are also no goods associated with the Gambling and Telecoms sectors. ↩
-
The estimates for trade in services for Civil Society are not covered in this release as there are no formally recognised imports or exports of services for this Sector from the data sources available. ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
HMRC (2020): UK overseas trade in goods statistics: summary of 2020 trade in goods. ↩
-
UK Trade in Services figures are taken from the UK Balance of Payments, The Pink Book: 2020. ↩
-
(ONS): Impact of the coronavirus and EU exit on the collection and compilation of UK trade statistics. ↩
-
(ONS): UK Perspectives 2016: Trade with the EU and beyond. ↩ ↩2
-
(ONS): International Passenger Survey methodology. ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5
-
(House of Commons library): Brexit timeline: events leading to the UK’s exit from the European Union ↩
-
(ONS): Impact of the coronavirus and EU exit on the collection and compilation of UK trade statistics. ↩
-
(ONS): Did UK firms stockpile items ahead of the Brexit deadline?. ↩
